The History, Evolution, & Technologies of Big Data [with use cases]
With the rising Big Data, Companies are moving towards Big Data tools and technologies. Everyone might want to know the history of big data. In this article, we will see the history of the present buzz “Big Data”.
The article will also cover the use cases of Big Data in different domains. You will also explore the different big data technologies adopted by companies for handling Big Data.
Let us start with the history of Big Data.
History of Big Data
The history of big data starts many years before the present buzz around Big Data. Seventy years ago the first attempt to quantify the growth rate of data in the terms of volume of data was encountered. That has popularly been known as “information explosion“.
We will be covering some major milestones in the evolution of “big data”.
1944:
Fremont Rider, based upon his observation, speculated that Yale Library in 2040 will have “approximately 200,000,000 volumes, which will occupy over 6,000 miles of shelves… [requiring] a cataloging staff of over six thousand persons.”
He did not predict the digitization of libraries but predicted the information explosion.
From 1944 to 1980, many articles and presentations were presented that observed the ‘information explosion’ and the arising needs for storage capacity.
1980:
In 1980, the sociologist Charles Tilly uses the term big data in one sentence “none of the big questions has actually yielded to the bludgeoning of the big-data people.” in his article “The old-new social history and the new old social history”.
But the term used in this sentence is not in the context of the present meaning of Big Data today.
Now, moving fast to 1997-1998 where we see the actual use of big data in its present context.
1997:
In 1977, Michael Cox and David Ellsworth published the article “Application-controlled demand paging for out-of-core visualization” in the Proceedings of the IEEE 8th conference on Visualization.
The article uses the big data term in the sentence “Visualization provides an interesting challenge for computer systems: data sets are generally quite large, taxing the capacities of main memory, local disk, and even remote disk. We call this the problem of big data. When data sets do not fit in main memory (in core), or when they do not fit even on local disk, the most common solution is to acquire more resources.”.
It was the first article in the ACM digital library that uses the term big data with its modern context.
1998:
In 1998, John Mashey, who was Chief Scientist at SGI presented a paper titled “Big Data… and the Next Wave of Infrastress.” at a USENIX meeting. John Mashey used this term in his various speeches and that’s why he got the credit for coining the term Big Data.
2000:
In 2000, Francis Diebold presented a paper titled “’ Big Data’ Dynamic Factor Models for Macroeconomic Measurement and Forecasting” to the Eighth World Congress of the Econometric Society.
In the paper, he stated that “Recently, much good science, whether physical, biological, or social, has been forced to confront—and has often benefited from—the “Big Data” phenomenon.
Big Data refers to the explosion in the quantity (and sometimes, quality) of available and potentially relevant data, largely the result of recent and unprecedented advancements in data recording and storage technology.”
He is the one who linked big data term explicitly to the way we understand big data today.
2001:
In 2001, Doug Laney, who was an analyst with the Meta Group (Gartner), presented a research paper titled “3D Data Management: Controlling Data Volume, Velocity, and Variety.” The 3V’s have become the most accepted dimensions for defining big data.
2005:
In 2005, Tim O’Reilly published his groundbreaking article “What is Web 2.0?”. In this article, Tim O’Reilly states that the “data is the next Intel inside”.
O’Reilly Media explicitly used the term ‘Big Data’ to refer to the large sets of data which is almost impossible to handle and process using the traditional business intelligence tools.
This is for sure the current widely understood form of Big data definition.
In 2005 Yahoo used Hadoop to process petabytes of data which is now made open-source by Apache Software Foundation. Many companies are now using Hadoop to crunch Big Data.
So we can say that 2005 is the year that the Big data revolution has truly begun and the rest they say is history.
Big Data Use Cases
It’s time to see some big data use cases. Many organizations use big data tools such as Apache Hadoop, Spark, Hive, Pig, etc. to handle big data and gain insights from it.
Below we listed some major big data use cases in different domains.
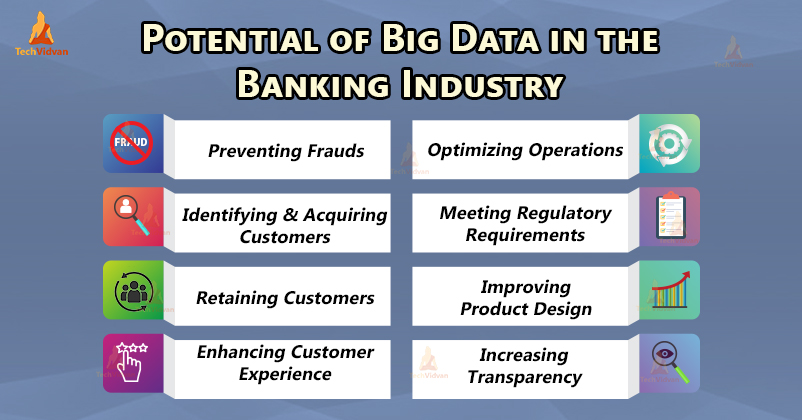
1. Financial Sectors
There are some applications of Big Data in the Finance and Banking sectors. Financial services organizations use big data for various:
a. Fraud Detection
Banks and Financial firms use big data analytics to differentiate legitimate business transactions and fraudulent interactions. Using machine learning and big data analysis, they were able to differentiate the normal activity and unusual behavior indicating fraud based on the customer’s history.
If unusual behavior is observed, the analysis systems will suggest immediate actions, such as blocking irregular transactions, which will stop fraud before it occurs.
b. Risk assessment
Financial firms manage their customer’s risk through big data analysis by analyzing their customer portfolios. The big data analysis supports real-time alerting, so if the risk threshold exceeds, the system alerts the firms.
c. Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is the best way to transform banks from product-centric to customer-centric businesses. Big Data enables banking sectors to group customers into distinct segments defined by data sets that include daily transactions, demographics, etc.
Marketing Campaigns and promotions are then targeted to the customers based on their segments.
Big Data in JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase is a topmost global financial services firm. It is among the largest banking institutions in the US. It generates massive amounts of data about its US-based customers such as credit card information and other transactional data.
Along with the publicly available economic statistics, JPMorgan Chase uses new big data analytics to develop insights into consumers’ trends and offers those reports to the bank’s clients.
JPMorgan Chase analyses phone calls, emails, transaction data to detect the possibilities of fraud. It also uses Analytics software developed by Palantir to keep an eye on employee communications to identify any risk of internal fraud.
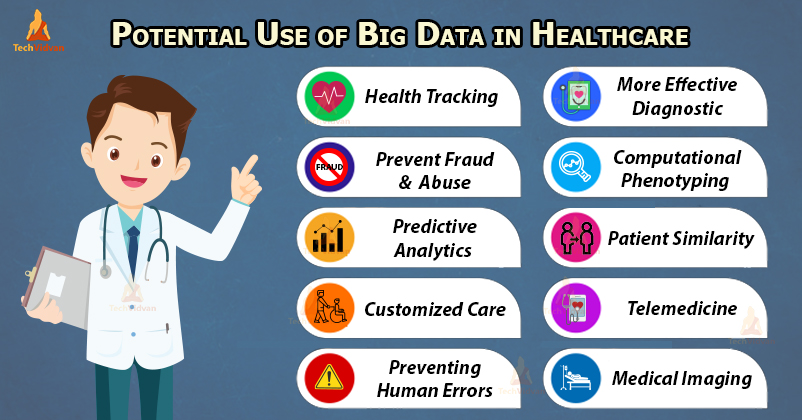
2. Health Care sectors
Many companies use big data, but the healthcare sector is one of the most popular areas where big data is getting profitable success in shaping the usual practices.
a. Patients predictions
Healthcare sectors use Big Data analysis to predict the numbers of next visits, to identify the frequency of skipped appointments, the full time of surgery.
Using big data analysis they can predict if doctors have enough medical supplies or not. Consequently, these process better quality of help to the patients which helps them to recover fast.
b. Real-Time Health Monitoring
With the advancement in IoT, there are many wearable devices like fitness trackers, wristbands, etc to monitor the health of their users. But with this monitoring device, it is needed to analyze the data generated by these devices to monitor user health in a real-time mode and provide the information to the doctors.
So, data from all these devices are analyzed instantly and, if something is wrong, an alert will be sent to the doctor or another specialist automatically. As a result, the doctor can contact the patient without any delay and provide them all the necessary instructions.
c. Predictions of Mass outbreaks
With big data analysis, a scientist builds social models of the health of the population. The doctors can create predictive models of outbreaks. By analyzing the data and using the algorithms, they were able to predict the disease outbreak.
So before the disease spread, the doctors were having the opportunity to create targeted vaccines faster which will prevent the disease outbreak. It is a wonderful benefit for the world’s population.
3. Big Data in Transportation industry
Not only is banking and medical, but big data is also proven profitable for the transportation industry as well. Big data is used in the transportation industries to make transportation more efficient and easy.
1. Route planning: Transportation firms are using big data to understand and estimate the users’ needs on different routes and on different modes of transportation. They make route planning to reduce their waiting time.
2. Congestion management and traffic control: Big data helps in combining real-time traffic data collected from road sensors, video cameras, and GPS devices. Thus, traffic problems in dense areas can be resolved by adjusting public transportation routes in real-time.
For example, people are using Google Maps to locate the least dense routes.
3. The safety level of traffic: The real-time processing of big data and predictive analysis can be used to identify accident-prone areas which can help in reducing accidents and increase the safety level of traffic.
4. Big Data in Government sector
Big data plays a vital role in the government sectors. Technologies in Big Data are playing significant roles in fields like public services, national security, defense, national security, cybersecurity, crime prediction, etc.
- In public services, Big data tools have a wide range of applications like financial market analysis, health-related search, fraud detection, environmental protection, financial market analysis, and many more.
- The Social Security Administration uses Big Data to analyze large amounts of social disability claims that arrive in unstructured format. This analytics helps SSA to fastly process medical information and helps in faster decision making and detecting fraudulent claims.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) uses big data for detecting and studying the patterns of food-related diseases and illnesses. This provides faster responses leading to rapid treatment and reduces death.
- The Department of Homeland Security also uses big data for various different use cases.
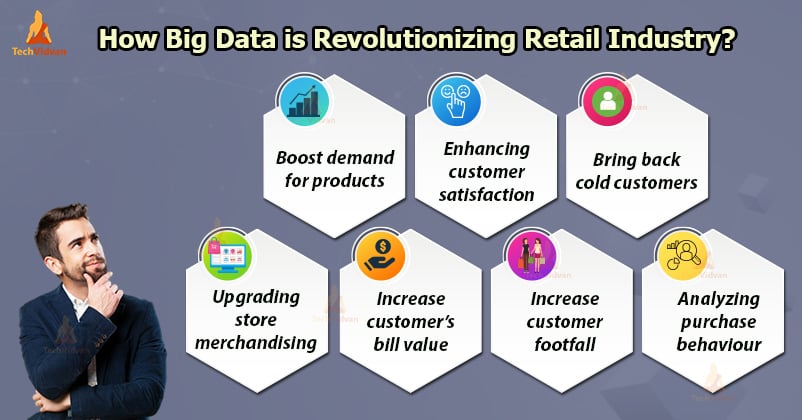
5. Big Data in Retail
Big Data analytics is playing a major role in shaping the future of the retail industries.
The retailers, both offline and online, are adopting the data analysis strategies for understanding the buying behavior of their customers, and mapping them to different products, and planning marketing strategies to sell out their products and increase their profits.
They are using big data analysis for:
1. Generating Recommendations: Retail industries based on their customer’s purchase history predicts what they will likely purchase next. They use machine learning models that are trained on historical data to make predictions.
2. Making Strategic Decisions: Retailers collect data from various sources and analyze them to make profitable decisions.
3. Market Basket Analysis: They use Market Basket Analysis techniques to figure out what products are most likely a customer would purchase together. Using Apache Hadoop, retailers now analyze vast amounts of data.
There are many other use cases of Big Data in different sectors like Education, Retail, Telecom, Media and Entertainment. Refer to Big Data Use Cases article to see different use cases of big data.
Big Data Technologies
Big Data technologies refer to the software utilities designed for the purpose of analyzing, processing, and extracting information from the vast amount of unstructured or semi-structured data that can’t be handled with the relational databases or the traditional processing systems.
The topmost big data technologies are:
1. Apache Hadoop
Hadoop provides the solution to all the big data problems. It is the backbone of the Big Data industry. 90% of the world’s data is now moved to Hadoop. It is the open-source software framework that stores and processes big data in a distributed manner.
The HDFS, MapReduce, and YARN are the core components of Hadoop.
2. Apache Spark
Apache Spark is another leading Big Data tool. Spark is a lightning-fast cluster computing engine that is 100 times faster than Hadoop in running applications in memory and 10 times faster than Hadoop in running applications in the disk.
Apache Spark is best known for its in-memory computing capabilities that deliver high-speed processing.
3. Apache Flink
Apache Flink is called 4G of Big Data. Flink is an open-source scalable data analytics framework that can handle stream processing as well as batch processing easily. It is a streaming data flow engine designed for stateful computations.
4. Tableau
Tableau is a BI tool for data visualization that transforms raw data into an understandable format. It visualizes data in the form of interactive dashboards that can be easily understood by any technical or non-technical user.
A person without any coding knowledge can learn Tableau. It is the most powerful and robust data visualization tool in the analytics industry.
5. QlikView
QlikView is another leading Big data visualization tool. It is the best option for transforming raw data into knowledge. It has a simple, clean and straightforward user interface that provides a completely new level of analysis.
6. Hive
A hive is an open-source tool that provides the developer the capability to use SQL like queries known as Hive Query Language to process Big Data. It is a data warehousing tool built on the top of Hadoop.
These are some top big data technologies that are used by a large number of companies for dealing with Big Data and to make profits with the rising Big Data market.
Summary
After reading this article, I hope you clearly understand how the term Big Data came into the IT market.
The article also enlisted the use case of big data in domains like the Finance sector, health care, and transportation industry. The article also described one case study on JPMorgan Chase.
Now you also have some little knowledge of Big Data popular technologies like Hadoop, Spark, Flink, Tableau, and many more.
I hope you are liking our efforts, do share this article with your friends. If you have any doubts in this Big Data evolution article then ask our TechVidvan experts.
Keep Learning!!