Features of Java Programming Language that justifies its Popularity
Java Features – Make use of Java Programming to its Fullest
Java is one of the most used programming languages, which allows the development of various types of applications that may run on a single machine. Having celebrated its 24th anniversary in 2019, Java has experienced a consistent development in its programming efficiency for decades.
Java has a design that incorporates flexibility, allowing developers to write code that would be able to run on any machine or device, irrespective of its architecture or platform. It is one of the most popular programming languages around the globe and is introduced to keep running on any stage consistently.
According to the Java home page, more than 1 billion computers and 3 billion mobile phones worldwide use Java for application development.
Why is Java so popular?
Java has become a popular and useful programming language because of its excellent features, which play a very important role in contributing to the popularity of this language. The Java features are called “Java BuzzWords”.
Sun MicroSystems officially describes Java with the following list of features:
- Simple and Familiar
- Compiled and Interpreted
- Platform Independent
- Portable
- Architectural Neutral
- Object-Oriented
- Robust
- Secure
- Distributed
- Multi-threaded and Interactive
- High Performance
- Dynamic and Extensible
Now, let’s discuss each of the above-listed features in detail.
Features of Java Programming Language
Here are the advanced features of Java programming in detail:
1. Simple and Familiar
Java is simple because:
Its coding style is very clean and easy to understand. It removes complexity because it doesn’t use complex and difficult features of other languages like C and C++, which are as follows:
- Concept of Explicit Pointers
- Storage classes
- Preprocessors and header files
- Multiple Inheritance
- Operator Overloading
- Goto Statements
Apart from the removal of these confusing and ambiguous concepts, there is a provision of Automatic Garbage Collection, in which there is no need to remove the unreferenced objects explicitly.
Java is familiar because:
- It has a base of familiar languages like C and C++ and contains many features of these languages.
- It removes the drawbacks, complexities and confusing elements of C/C++. So if you have good knowledge of C/C++, you will find Java familiar and easy to understand.
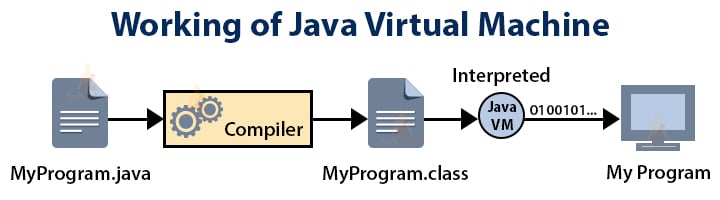
2. Compiled and Interpreted
Usually, a computer language can be either compiled or interpreted. Java integrates the power of Compiled Languages with the flexibility of Interpreted Languages.
Java compiler (javac) compiles the java source code into the bytecode.
Java Virtual Machine (JVM) then executes this bytecode which is executable on many operating systems and is portable.
The diagram below shows the above process:
3. Platform Independent
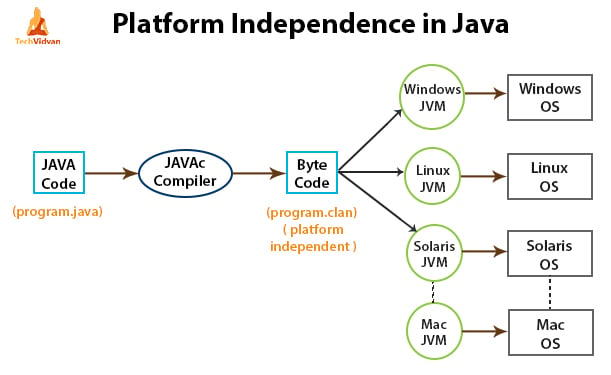
The most significant feature of Java is that it provides platform independence which leads to a facility of portability, which ultimately becomes its biggest strength.
Being platform-independent means a program compiled on one machine can be executed on any machine in the world without any change. Java achieves platform independence by using the concept of the BYTE code.
The Java compiler never converts the source code to machine code like that of the C/C++ compiler.
Instead, it converts the source code into an intermediate code called the byte code and this byte code is further translated to machine-dependent form by another layer of software called JVM (Java Virtual Machine).
Therefore, JVM can execute bytecode on any platform or OS on which it is present, regardless of the fact that on which machine the bytecode was generated.
This is where the “Write Once, run anywhere” (WORA) slogan for Java comes in, which means that we can develop applications on one environment (OS) and run on any other environment without doing any modification in the code.
Below diagram explains the platform independence feature of Java-
4. Portable
Java is “portable” refers to the SE (Standard Edition) version. The portability actually comes from architecture-neutrality.
In C/C++, the source code may run slightly differently on different hardware platforms, but Java simplifies it. You can run Java bytecode on any hardware that has a compliant JVM which can convert the bytecode according to that particular machine.
In Java, the size of the primitive data types is machine-independent, which were dependent in the case of C/C++. So, these provisions make Java programs portable among different platforms such as Windows, Unix, Solaris, and Mac.
Moreover, any changes and updates made in Operating Systems, Processors and System resources will not enforce any changes in Java programs.
5. Architectural Neutral
This buzzword means that the program written on one platform or OS is independent of other platforms or environments and can run on any other Operating System without recompiling them.
In other words, it is based on the ‘Write-once-run-anywhere’ (WORA) or ‘Write-once-run-everywhere’ (WORE) approach.
Byte-code is not dependent on any machine architecture and Java Virtual Machine (JVM) can easily translate bytecode into a machine-specific code.
This feature is very useful when we develop applets or download applications from the Internet.
Moreover, these applications need to run on different machines, so this feature proves to be very important in this case.
6. Object-Oriented
Next in Java features article, we will discuss the OOP feature. Java strongly supports the concepts of Object-Oriented Programming due to which it is called a pure object-oriented language.
Java supports major Object-Oriented programming features like Encapsulation, Abstraction, and Inheritance.
Almost everything in Java is an object. All programs and data live within objects and classes. ‘Objects’ model Java rather than the ‘processes’. Java comes with an extensible set of classes organized in packages.
For example, we cannot develop an executable program in Java without making use of the class. This indicates that Java very strictly applies the principle of Encapsulation.
7. Robust
Java is robust as it is capable of handling run-time errors, supports automatic garbage collection and exception handling, and avoids explicit pointer concept.
Java has a strong memory management system. It helps in eliminating errors as it checks the code during both compile and runtime.
Java is garbage-collected language – JVM automatically deallocates the memory blocks and programmers do not have to worry about deleting the memory manually as in case of C/C++.
Java also provides the concept of exception handling which identifies runtime errors and eliminates them.
In Java, any runtime error encountered by the JVM is never passed directly to the underlying system rather immediately terminates the program stopping it from causing any harm to the underlying system.
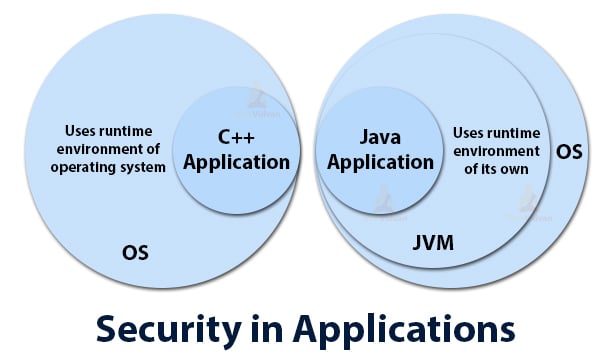
8. Secure
Security is an important issue for any programming language as there is a threat of malicious activities and viruses. Java supports access modifiers to check memory access and also ensures that no viruses enter an applet.
Java is a more secure language as compared to C/C++, as it does not allow a programmer to explicitly create pointers. Thus in Java, we can not gain access to a particular variable if we do not initialize it properly.
Programs run in a virtual machine sandbox – A separate environment that allows users to execute their applications without affecting the underlying system.
It has a bytecode verifier that checks the code fragments for any illegal code that violates the access right.
9. Distributed
Java is distributed because it encourages users to create distributed applications.
In Java, we can split a program into many parts and store these parts on different computers. A Java programmer sitting on a machine can access another program running on the other machine.
This feature in Java gives the advantage of distributed programming, which is very helpful when we develop large projects. Java helps us to achieve this by providing the concept of RMI (Remote Method Invocation) and EJB (Enterprise JavaBeans).
Java comes with an extensive library of classes for interacting, using TCP/IP protocols such as HTTP and FTP, which makes creating network connections much easier than in C/C++.
It also enables multiple programmers at many locations to work together on a single project.
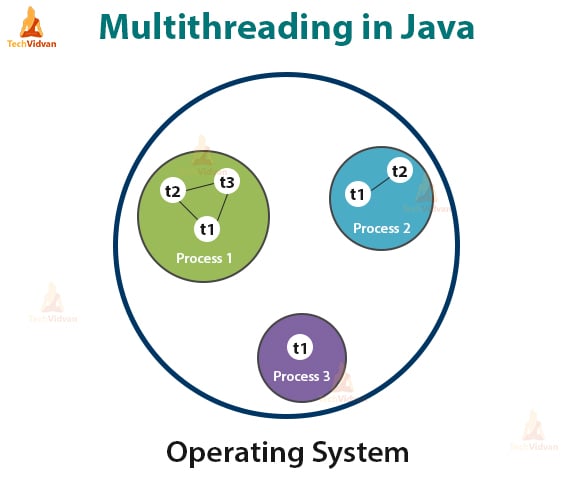
10. Multi-threaded and Interactive
A thread is an independent path of execution within a program, executing concurrently. Multithreaded means handling multiple tasks simultaneously or executing multiple portions (functions) of the same program in parallel.
The code of java is divided into smaller parts and Java executes them in a sequential and timely manner.
Advantages:
- The main advantage of multithreading is that the maximum utilization of resources is possible.
- It doesn’t occupy memory for each thread. It shares a common memory area.
- There is no need to wait for the application to finish one task before beginning another one.
- There is a decreased cost of maintenance. Also, It is time-saving.
- It improves the performance of complex applications.
Java is interactive because its code supports effective CUI (Character User Interface) and GUI (Graphical User Interface) programs. It greatly improves the interactive performance of graphical applications.
11. High Performance
The performance of Java is impressive for an interpreted language because of its intermediate bytecode.
Java provides high performance with the use of “JIT – Just In Time compiler”, in which the compiler compiles the code on-demand basis, that is, it compiles only that method which is being called. This saves time and makes it more efficient.
Java architecture is also designed in such a way that it reduces overheads during runtime. The inclusion of multithreading enhances the overall execution speed of Java programs.
Bytecodes generated by the Java compiler are highly optimized, so Java Virtual Machine can execute them much faster.
12. Dynamic and Extensible
Java is dynamic and extensible means with the help of OOPs, we can add classes and add new methods to classes, creating new classes through subclasses. This makes it easier for us to expand our own classes and even modify them.
Java gives the facility of dynamically linking new class libraries, methods, and objects. It is highly dynamic as it can adapt to its evolving environment.
Java even supports functions written in other languages such as C and C++ to be written in Java programs. These functions are called “native methods”. These methods are dynamically linked at runtime.
Summary
Overview of Java is incomplete without looking at the “Java buzzwords”. Java is designed from the features inherited from C and C++ and polishes their features to improve the current scenario of programming.
From the discussion, we can clearly understand how advanced Java features play a crucial role in making it so popular among users and developers. So, the fact that major corporations are using Java is clear from this article.
Responding to the rise of the online environment, Java offers features that allow smooth programming for a highly distributed architecture. These features of Java are more than enough to explain the importance of Java.
If you want to add any other essential feature of Java, do mention in the comment section.