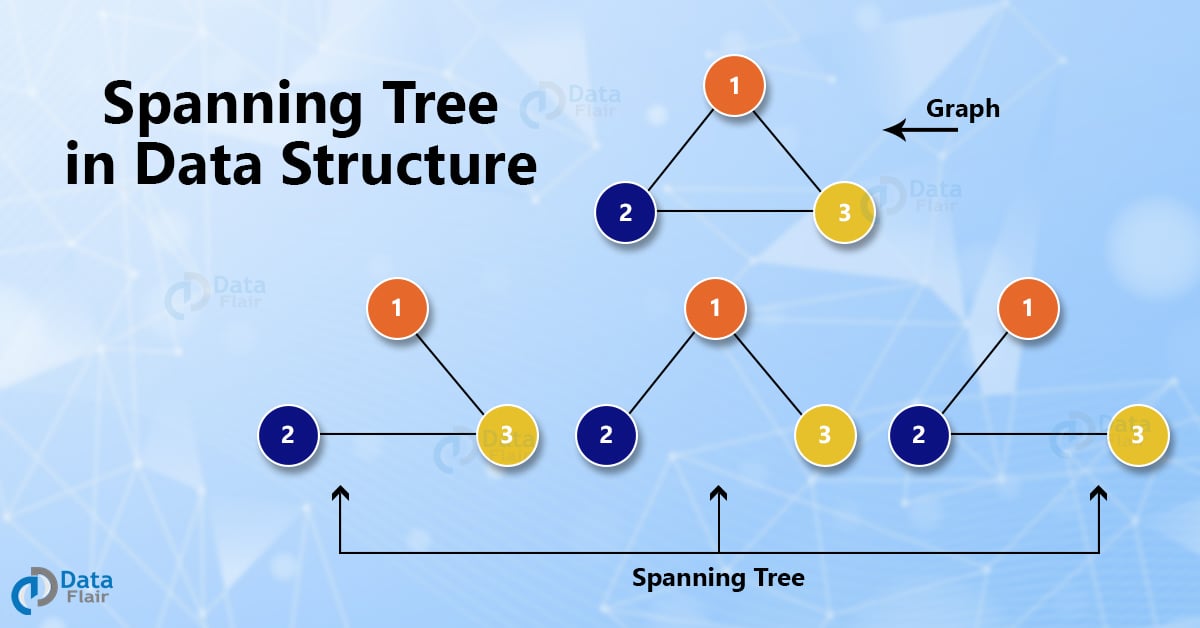
A spanning tree is a tree that connects all the vertices of a graph with the minimum possible number of edges. Thus, a spanning tree is always connected. Also, a spanning tree never contains a cycle. A spanning tree is always defined for a graph and it is always a subset of that graph. Thus, a disconnected graph can never have a spanning tree.
Spanning Trees Terminologies:
1. Connected Graph: A connected graph is a graph in which we can reach any vertex from any vertex. Thus, in a connected graph, all vertices are connected to each other through at least one path.
2. Undirected Graph: It is a graph in which the edges don’t have a particular direction. In an undirected graph, the edges are bidirectional.
3. Directed Graph: In this case, the edges are unidirectional. Thus, we can go from only one end to the other ends. For every edge, there is an associated direction.
4. Simple graph: A simple graph is a graph that does not contain cycles and loops.
Defining a Spanning Tree:
Every undirected and connected graph has a minimum of one spanning tree. Consider a graph having V vertices and E number of edges. Then, we will represent the graph as G(V, E). Its spanning tree will be represented as G’(V, E’) where E’ ⊆ E and the number of vertices remain the same. So, a spanning tree G’ is a subgraph of G whose vertex set is the same but edges may be different.
Example:
Consider the following undirected, simple and connected graph G having 4 vertices: A, B, C and D.
There are many spanning trees possible for this graph. Some of them are shown below:
The above graph G was a complete graph having 4 vertices. For any complete graph, the number of spanning trees is nn-2. Thus, in the worst case, the number of spanning trees formed is of the order O(n2).
General Properties of Spanning Trees:
- There can be more than one spanning tree possible for an undirected, connected graph.
- In the case of directed graphs, the minimum spanning tree is the one having minimum edge weight.
- All the possible spanning trees of a graph have the same number of edges and vertices.
- A spanning tree can never contain a cycle.
- Spanning tree is always minimally connected i.e. if we remove one edge from the spanning tree, it will become disconnected.
- A spanning tree is maximally acyclic i.e. if we add one edge to the spanning tree, it will create a cycle or a loop.
- It is possible to have more than one minimum spanning tree if the graph weights of some edges are the same.
- Any connected and undirected graph will always have at least one spanning tree.
Mathematical Properties of Spanning Trees:
- For any complete graph, the number of spanning trees is nn-2.
- In a complete graph, we can create a spanning tree by removing a maximum of E-N+1 edges. Here, E = Number of edges and N = Number of nodes/vertices.
- For a simple connected graph, its spanning tree will have N-1 edges, where N is the number of vertices.
Minimum Spanning Tree:
A minimum spanning tree is defined for a weighted graph. A spanning tree having minimum weight is defined as a minimum spanning tree. This weight depends on the weight of the edges. In real-world applications, the weight could be the distance between two points, cost associated with the edges or simply an arbitrary value associated with the edges.
Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms:
There are various algorithms in computer science that help us find the minimum spanning tree for a weighted graph. Some of these algorithms are:
1. Prim’s Algorithm
2. Kruskal’s Algorithm
3. Both these algorithms follow the greedy approach to find the minimum cost spanning tree.
Applications of Spanning Tree:
- For implementing Routing protocols in computer networks
- In civil network planning to build networks
- For clustering i.e. grouping similar objects under one category and distinguishing from other categories
Applications of Minimum Spanning Tree:
- In designing telecommunication networks and water supply networks
- For finding paths in a map
- In electrical grid systems
Conclusion:
In this article, we have seen what is a spanning tree and what is a minimum spanning tree. We have also seen their examples and applications. The article also covers the general as well as mathematical properties of spanning trees.