Expert Systems in AI – Components, Applications and Characteristics
Expert System is an intuitive and dependable PC based dynamic framework that utilizes the two realities and heuristics to take care of complex dynamic issues.
An expert system in AI may be a computing system that emulates the decision-making ability of a person’s expert. It is considered at the most elevated level of human knowledge and mastery. The reason for a specialist framework is to unravel the most complex problems arising in any particular domain.
In this tutorial, we are going to learn Expert systems in AI.
History of Expert Systems in AI
Expert Systems were first presented by Stanford University specialists during the 1970s, in spite of the fact that it has been on PC researchers’ psyches since the mid-1940s and 1950s.
Edward Feigenbaum and Joshua Lederberg, who were key individuals from the Stanford Heuristic Programming Project, built up the principal master framework in 1965. The analysts needed to make a specific framework instead of a universally useful one.
One of the gadget’s initial applications included synthetic examination (DENDRAL) and clinical diagnostics (MYCIN). MYCIN, an irresistible infection diagnostics device, makes findings through reverse affixing.
Master frameworks have clarification offices that let clients ask them how they arrived at a specific resolution or why they couldn’t. All things considered, its equipped for legitimizing its thinking and yield.
Examples of AI Expert Systems
1. MYCIN
MYCIN is amongst the oldest expert systems. It was designed upon the fundamental of backward chaining and was capable to identify infection-causing bacteria.
MYCIN treats certain bacterial infections and controls acne, additionally to other acne treatments. It prevents infections in people with a history of rheumatic disease, congenital heart condition or other acquired valvular heart condition and who are allergic to penicillin antibiotics.
2. DENDRAL
An expert system designed to determine the structure of the chemical using its spectrographic data. Its primary aim was to review hypothesis formation and discovery in science.
The software program DENDRAL is said to be the primary expert system because it automated the decision-making process and problem-solving behavior of organic chemists.
3. R1/XCON
An Expert System that had the ability to select the best-suited software to perform a particular task assigned by the user.
A system that ensured the customer was furnished with all the components and software that was needed to form up the required computing system that that they had ordered.
4. PXDES
Pneumoconiosis X-Ray Diagnosis Expert System (PXDES) is an expert system which is used to diagnose in which stage a patient of lung cancer. The shadow is employed to work out the sort and degree of carcinoma .
5. DXplain
This was an expert system that was capable of diagnosing a number of diseases in a patient based on the input provided.
DXplain provides information and supplies clinical manifestations, if any, for diseases that are unusual or atypical.
Characteristics of Expert Systems in AI
1. High performance
The first and foremost characteristic of an expert system is to deliver high performance 24×7
2. Understandable
The expert system should be easy to comprehend for all the people using it.
3. Reliable
An expert system has to be reliable in the sense that it is error-free so that it is trustable.
4. Highly Responsive
An expert system has to be proactive and provide responses for each and every detail of the problem.
Why Expert Systems
- It has huge data storage capacity and can rely upon to recall that data after any duration if need be.
- It puts to use the collaborative knowledge of experts of a domain in order to provide the best possible output.
- The information stored in the knowledge bank is highly secure in nature.
- It provides output 24×7 and is emotionless and thus can’t feel stress.
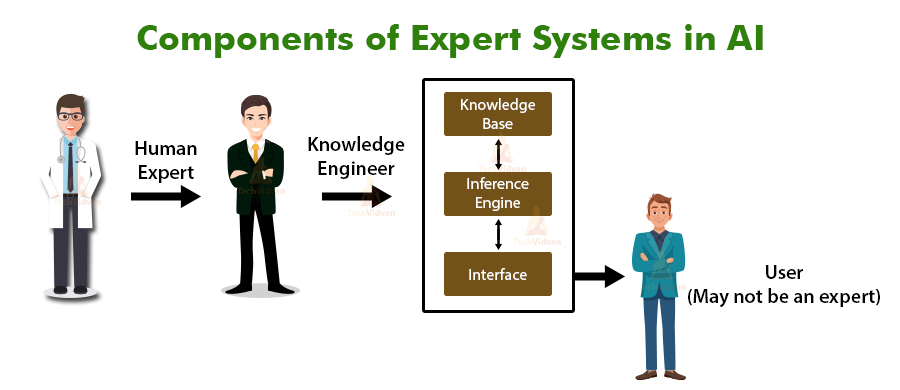
Components of Expert Systems
Let us see the components of expert systems in AI:
1. User Interface(UI)
With the assistance of a UI, the master framework communicates with the client, accepts inquiries as a contribution to a clear arrangement, and passes it to the deduction motor.
In the wake of getting the reaction from the deduction motor, it shows the yield to the client. As it were, it is an interface that helps a non-master client to speak with the master framework to discover an answer.
It takes the client’s inquiry in a coherent structure and forwards it to the inference engine. From that point onward, it shows the outcomes to the client, as such, it’s an interface that enables the client to speak with the master framework.
The (UI) is the space that encourages correspondence between the framework and its clients. It’s synonymous with your PC work area or cell phone home screen.
2. Inference Engine
Inference Engine is the mind behind the UI. It contains a predefined set of rules to tackle a particular issue and alludes to the information from the Knowledge Base.
It chooses realities and rules to apply when attempting to answer the client’s inquiry. Inference Engine gives thinking about the data in the information base.
It likewise helps in deducting the issue to discover the arrangement. This part is additionally useful for detailing ends.
The two basic strategies used in inference engines are:
a. Forward Chaining
This strategy used to determine the probable outcome in the future. With the given inputs and conditions, this strategy utilizes expert systems to find out the probable outcome. This helps to extract data till a particular goal is reached.
b. Backward Chaining
This strategy used to determine why would a particular event take happen with the current circumstances provided. It is utilized in automated theorem provers, inference engines, proof assistants, and other AI applications
3. Knowledge Base
It is where data contributed by specialists from the required domains is put away. Think about an information base as a book or an article.
To make entries from a book sound, you need to refer to data from specialists to make it more credible. It contains both factual and heuristic knowledge.
Components of Knowledge Base
a. Factual Knowledge
As the name suggests, factual knowledge is based upon facts. Information in the form of facts are proven and widely accepted by one and all.
b. Heuristic Knowledge
While Factual Knowledge is about facts, heuristic knowledge is unorganized in nature and relies on one’s own evaluation.
Applications of Expert Systems
- Expert systems are being used in designing and manufacturing domain for the production of vehicles and gadgets like cameras.
- In the knowledge domain, Expert Systems are used for delivering the required knowledge to the client. The knowledge can be legal advice, tax advice, or something other than that.
- In the banking and finance sector, expert systems are widely used for the detection of frauds.
- Expert Systems can also use in the diagnosis and troubleshooting of medical equipment.
- Apart from this, Expert Systems can also have use cases in Planning and Scheduling tasks.
Advantages of Expert Systems
- Expert Systems are easily available as they are not so difficult to develop and are thus easier to reproduce.
- Increased accuracy is a prominent advantage of Expert Systems.
- They can be of use at workstations where there is a risk to human lives.
- They can be made to work 24×7 without the need for any human intervention.
- Expert Systems offer a very speedy decision-making process which in most cases is error-free.
Limitations of Expert Systems
- Its judgment is based solely on the information being stored in the knowledge base. Any discrepancy in the information can lead to flawed decision making.
- Unlike humans, it is not capable of providing an out of the box solution for problems
- The cost required for the maintenance of these systems is quite hefty.
Summary
In conclusion, these are some of the details about Expert Systems in AI. Expert systems offer great speed and reduces the quantity of labor. Generally, a mistake rate of the expert system is low as compared to human errors. They can be utilized in any risky environments where humans cannot work with.
Though it has a lot of benefits, still limitations like the high cost of maintenance are a hurdle in its widespread application.
With time, as these limitations are countered, Expert Systems would witness an even greater adoption across industries.