Advantages and Disadvantages of Java
Java has been consistently holding the top position of the TIOBE index among all other programming languages. Though many new languages have been discovered, the fame of Java never goes down. Java has been ruling over all other languages for more than 20 years.
The majority of experts cannot deny the fact that Java is one of the most powerful and effective languages ever created and is the most widely used programming language in many areas.
But, we also know that every coin has two sides; similarly, Java can not run away from this fact and therefore it has also got its own limitations and benefits; what we call it is a pros and cons of Java.
In this article, we will acquaint you with the prominent advantages and disadvantages of Java, which will help you have a clear vision of this language.
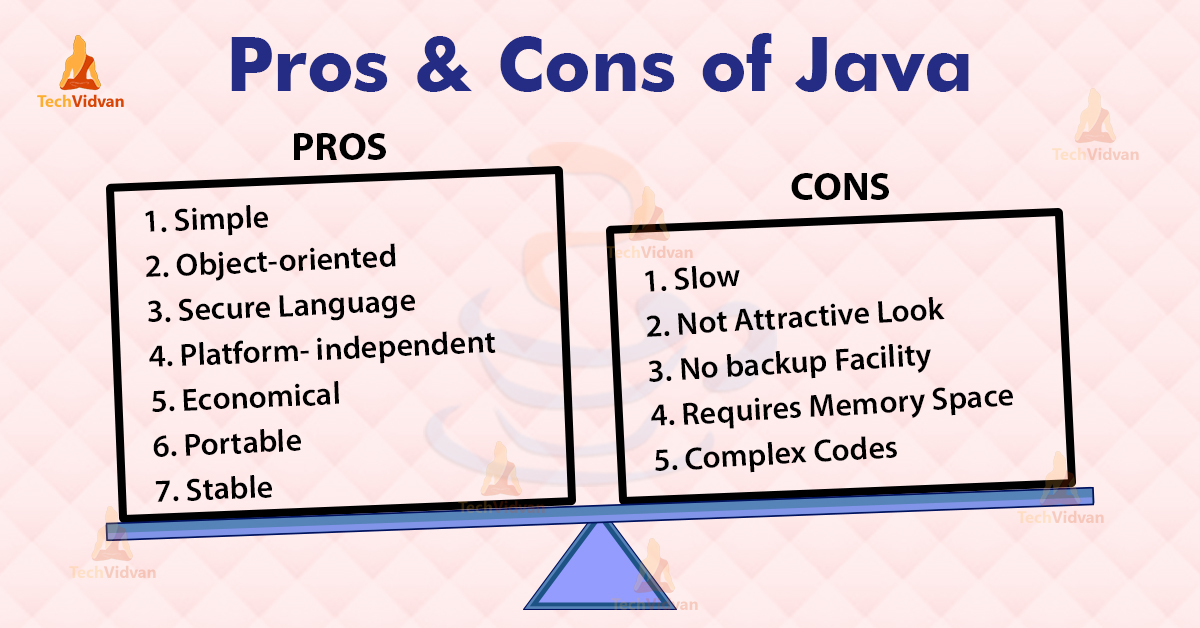
Advantages of Java
Java is an Object-Oriented and a general-purpose programming language that helps to create programs and applications on any platform. Java comes up with a bundle of advantages that lets you stick with it.
Let’s discuss the pros of using Java programming language.
1. Java is Simple
Any language can be considered as simple if it is easy to learn and understand. The syntax of Java is straightforward, easy to write, learn, maintain, and understand, the code is easily debuggable.
Moreover, Java is less complex than the languages like C and C++, because many of the complex features of these languages are being removed from Java such as explicit pointers concept, storage classes, operator overloading, and many more.
2. Java is an Object-Oriented Programming language
Java is an object-oriented language that helps us to enhance the flexibility and reusability of the code. Using the OOPs concept, we can easily reuse the object in other programs.
It also helps us to increase security by binding the data and functions into a single unit and not letting it be accessed by the outside world. It also helps to organize the bigger modules into smaller ones so they are easy to understand.
3. Java is a secure language
Java reduces security threats and risks by avoiding the use of explicit pointers. A pointer stores the memory address of another value that can cause unauthorized access to memory.
This issue is resolved by removing the concept of pointers. Also, there is a Security manager in Java for each application that allows us to define the access rules for classes.
4. Java is cheap and economical to maintain
Java programs are cheap to develop and maintain as these programs are dependent on a specific hardware infrastructure to run. We can easily execute them on any machine that reduces the extra cost to maintain.
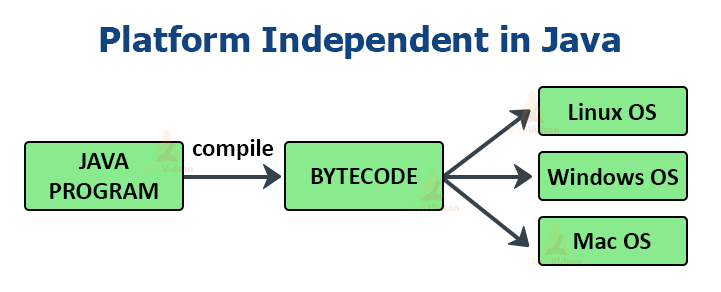
5. Java is platform-independent
Java offers a very effective boon to its users by providing the feature of platform independence that is Write Once Run Anywhere(WORA) feature.
The compiled code, i.e the byte code of java is platform-independent and can run on any machine irrespective of the operating system. We can run this code on any machine that supports the Java Virtual Machine(JVM) as shown in the figure below:
6. Java is a high-level programm4ing language
Java is a high-level programming language as it is a human-readable language. It is similar to human language and has a very simple and easy to maintain syntax that is similar to the syntax of C++ language but in a simpler manner.
7. Java supports portability feature
Java is a portable language due to its platform independence feature. As the Java code can be run on any platform, it is portable and can be taken to any platform and can be executed on them. Therefore Java also provides the advantage of portability.
8. Java provides Automatic Garbage Collection
There is automatic memory management in Java that is managed by the Java Virtual Machine(JVM).
Whenever the objects are not used by programs anymore and they do not refer to anything that they do not need to be dereferenced or removed by the explicit programming.
Java automatically removes the unused objects with the help of the automatic Garbage Collection process.
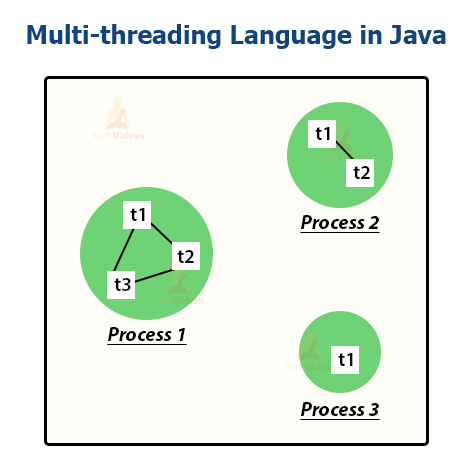
9. Java supports Multithreading
Java is a multithreaded language that is in Java more than one thread can run at the same time. A thread is the smallest unit of a process. Multithreading helps us to gain the maximum utilization of CPU.
Multiple threads share a common memory area and increase the efficiency and performance of the application. These threads run independently of each other without affecting each other.
10. Java is stable
Java programs are more stable as compared to programs of other languages. Moreover, a new version of Java is released in no time with more advanced features which makes it more stable.
11. Java is a distributed language
Java is a distributed language as it provides a mechanism for sharing data and programs among multiple computers that improve the performance and efficiency of the system.
The RMI(Remote Method Invocation) is something that supports the distributed processing in Java. Moreover, Java also supports Socket Programming and the CORBA technology that helps us to share objects in a distributed environment.
12. Java provides an efficient memory allocation strategy
Java has an efficient memory allocation strategy as it divides the memory mainly in two parts- Heap Area and Stack Area.
The JVM provides us the memory space for any variable either from the heap area or the stack area. Whenever we declare a variable JVM gives memory from either stack or heap space.
Disadvantages of Java
To start learning or working upon any programming language you must know its strengths and weaknesses so that you can utilize the best things out of it and avoid causing the circumstances that portray in the bad side of the language.
Java has also got some drawbacks that you should know before starting over. Let’s discuss the cons of using Java.
1. Java is slow and has a poor performance
Java is memory-consuming and significantly slower than native languages such as C or C++. It is also slow compared to other languages like C and C++ because each code has to be interpreted to the machine level code.
This slow performance is due to the extra level of compilation and abstraction by the JVM. Moreover, sometimes the garbage collector leads in the poor performance of Java as it consumes more CPU time
2. Java provides not so attractive look and feels of the GUI
Though there are many GUI builders in Java for creating the graphical interface still they are not suitable for creating complicated UI. There are many inconsistencies while using them.
There are many popular frameworks such as Swing, SWT, JavaFX, JSF for creating GUI. But they are not mature enough to develop a complex UI. Choosing one of them which can be suitable for you may require additional research.
3. Java provides no backup facility
Java mainly works on storage and not focuses on the backup of data. This is a major drawback that makes it lose the interest and ratings among users.
4. Java requires significant memory space
Java requires a significant or major amount of memory space as compared to other languages like C and C++. During the execution of garbage collection, the memory efficiency and the performance of the system may be adversely affected.
5. Verbose and Complex codes
Java codes are verbose, meaning that there are many words in it and there are many long and complex sentences that are difficult to read and understand. This can reduce the readability of the code.
Java focuses on being more manageable but at the same time, it has to compromise it with the overly complex codes and long explanations for each thing.
Conclusion
So here we come to the end of discussion on the pros and cons of Java. There are more advantages of java as compared to Java drawbacks.
Besides all the above limitations of Java, it is one of the most used languages in the software industry due to its platform independence, security, and maintainability features.
From this article, you can easily compare Java with other languages on the basis of its virtues and drawbacks.