How to Read Excel File in Java Using POI
In this TechVidvan Java Tutorial, we are going to learn how we can read excel file in java. In Java, reading excel files is not similar to reading word files because of cells in excel files.
JDK does not provide a direct API to read or write Microsoft Excel or Word documents. We have to rely on the third-party library that is Apache POI. In this article, we will learn how to create and write to an excel file using Apache POI.
Reading and writing Excel Files in Java
The people all over the world use excel files (spreadsheets) for various tasks related to organization, analysis, and storage of tabular data. Since these excel files are so common, the developers often face some use-cases when we need to read data from an excel file or generate a report in excel format.
Apache POI (Poor Obfuscation Implementation) is a Java API for reading and writing Microsoft Documents in both formats .xls and .xlsx. It contains classes and interfaces.
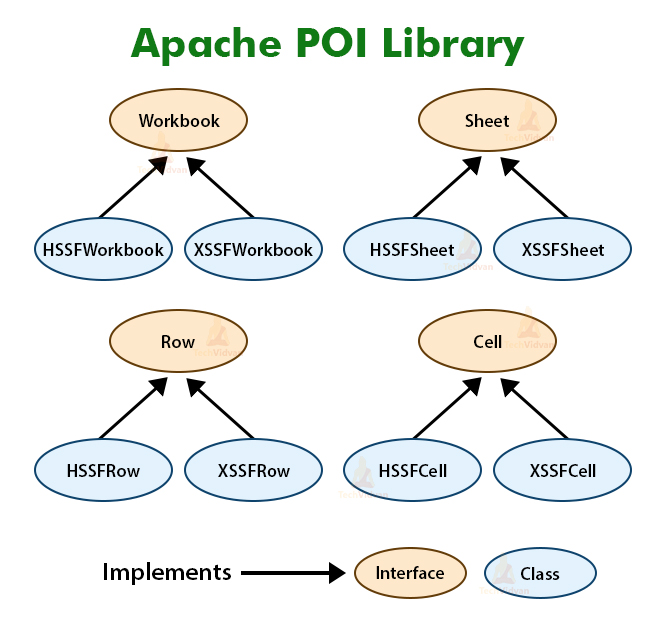
Apache POI Library
The Apache POI library provides two implementations for reading excel files:
1. HSSF (Horrible SpreadSheet Format) Implementation
It denotes an API that is working with Excel 2003 or earlier versions. There are interfaces of HSSF implementations which are HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet, HSSFRow, and HSSFCell. We use these interfaces work with excel files of the older binary file format – .xls
2. XSSF (XML SpreadSheet Format) Implementation
It denotes an API that is working with Excel 2007 or later versions. We can use the XSSF implementation to work with the newer XML based file format – .xlsx.
Interfaces and Classes in Apache POI
Below are various interfaces in POI:
1. Workbook: It represents an Excel Workbook. It is an interface implemented by HSSFWorkbook and XSSFWorkbook.
2. Sheet: It is an interface that represents an Excel worksheet. A sheet is a central structure of a workbook, which represents a grid of cells. The Sheet interface extends java.lang.Iterable.
3. Row: It is also an interface that represents the row of the spreadsheet. The Row interface extends java.lang.Iterable. There are two concrete classes: HSSFRow and XSSFRow.
4. Cell: It is an interface. It is a high-level representation of a cell in a row of the spreadsheet. HSSFCell and XSSFCell implement the Cell interface
Steps to Read Data from XLS file
1. Create a simple Java project in eclipse.
2. Now, create a lib folder in the project.
3. Download and add the following jar files in the lib folder:
- commons-collections4-4.1.jar Click Here
- poi-3.17.jar Click Here
- poi-ooxml-3.17.jar Click Here
- poi-ooxml-schemas-3.17.jar Click Here
- xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar Click Here
4. Set the Class-Path:
Right-click on the project ->Build Path ->Add External JARs -> select all the above jar files -> Apply and close.
5. Now create a class file with the name ReadExcelFileDemo and write the following code in the file.
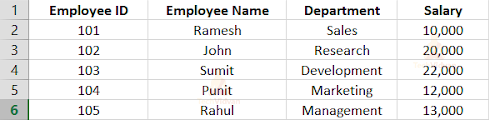
6. Create an excel file with the name “employee.xls” and write some data into it.
Code to read excel file
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.FormulaEvaluator;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
public class ReadExcelFileDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
//obtaining input bytes from a file
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\mysheets\\employee.xls"));
//creating workbook instance that refers to .xls file
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fis);
//creating a Sheet object to retrieve the object
HSSFSheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
//evaluating cell type
FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator = wb.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator();
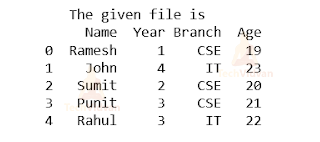
System.out.println(“The given file is”);
for (Row row: sheet)
//iteration over row using for each loop
{
for (Cell cell: row) //iteration over cell using for each loop
{
switch (formulaEvaluator.evaluateInCell(cell).getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
//field that represents numeric cell type
//getting the value of the cell as a number
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "\t\t");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
//field that represents string cell type
//getting the value of the cell as a string
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "\t\t");
break;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:
Code to read .xlsx file
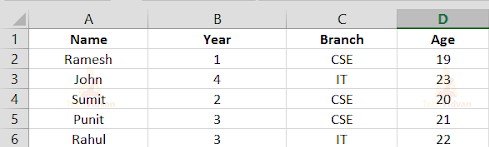
The xlsx file is same as xls file and looks like:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class XLSXReaderExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File file = new File("C:\\mysheets\\student.xlsx");
//creating a new file instance
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//obtaining bytes from the file
//creating Workbook instance that refers to .xlsx file
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
XSSFSheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
//creating a Sheet object to retrieve object
Iterator < Row > itr = sheet.iterator();
//iterating over excel file
System.out.println(“The given file is”);
while (itr.hasNext()) {
Row row = itr.next();
Iterator < Cell > cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
//iterating over each column
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
//field that represents string cell type
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "\t\t\t");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
//field that represents number cell type
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "\t\t\t");
break;
default:
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output:
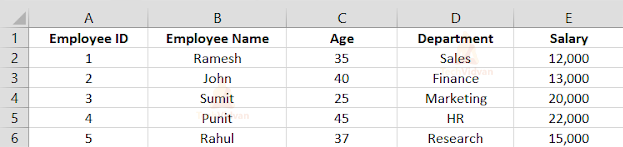
Reading a particular cell value from an excel file (.xlsx)
Table: EmployeeData.xlsx
Example
In the following example, we read the value of the 2nd row and the 2nd column. The row and column counting start from 0. So the program returns “John”.
Code to read a particular cell from an excel file
//reading value of a particular cell
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel. * ;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class ReadCellExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReadCellExample rc = new ReadCellExample(); //object of the class
//reading the value of 2nd row and 2nd column
String vOutput = rc.ReadCellData(2, 2);
System.out.println(vOutput);
}
//method defined for reading a cell
public String ReadCellData(int vRow, int vColumn) {
String value = null; //variable for storing the cell value
Workbook wbook = null; //initialize Workbook null
try {
//reading data from a file in the form of bytes
FileInputStream fis = FileInputStream("C:\\mysheets\\EmployeeData.xlsx");
//creates an XSSFWorkbook object by buffering the whole stream into the memory
wbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
Sheet sheet = wbook.getSheetAt(0);
//getting the XSSFSheet object at given index
Row row = sheet.getRow(vRow);
//returns the logical row
Cell cell = row.getCell(vColumn);
//getting the cell representing the given column
value = cell.getStringCellValue();
//getting cell value
return value;
//returns the cell value
}
}
Output:
John
How to Write Excel File in Java
Writing excel using POI is very simple and involves the following steps:
1. Create a workbook
2. Create a sheet in a workbook
3. Create a row in a sheet
4. Add cells in a sheet
5. Now, repeat the steps 3 and 4 to add more data
Code to write excel file in Java using POI
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel. * ;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class WriteExcelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Blank workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//Create a blank sheet
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Product data");
//This data needs to be written (Object[])
Map < String,
Object[] > data = new TreeMap < String,
Object[] > ();
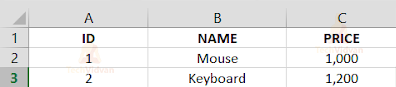
data.put("1", new Object[] {
"ID",
"NAME",
"PRICE"
});
data.put("2", new Object[] {
1,
"Mouse",
1000
});
data.put("3", new Object[] {
2,
"Keyboard",
1200
});
//Iterate over data and write to sheet
Set < String > keyset = data.keySet();
int rownum = 0;
for (String key: keyset) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++);
Object[] objArr = data.get(key);
int cellnum = 0;
for (Object obj: objArr) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++);
if (obj instanceof String) cell.setCellValue((String) obj);
else if (obj instanceof Integer) cell.setCellValue((Integer) obj);
}
}
try {
//Write the workbook in file system
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("Product.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx written successfully on disk.");
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we learned how to read and write an excel file in Java using the program. There is a library called Apache POI which has many classes and methods that help us to deal with excel files in Java.
We studied how to read a xls file and a xlsx file and how to write an excel file. We can also access a particular cell of an excel file.
Do share feedback in the comment section if you liked the article.