Python NumPy Tutorial for Data Science
In this NumPy Tutorial, we will learn what is NumPy. We will learn about its uses, installation, operations and many other features.
So let’s start!!!
NumPy Introduction
NumPy stands for ‘Numerical Python’. It is a package in Python to work with arrays. It is a basic scientific library. Its most important feature is the n-dimensional array object. It has uses in statistical functions, linear algebra, arithmetic operations, bitwise operations, etc.
We perform all the operations on the array elements. We can initialize these arrays in several ways.
Prerequisite to Learn NumPy
The two basic prerequisites for NumPy are Python and Mathematics. We need to know the python basics to work with the NumPy module.
The functions available in NumPy are built on python language. We can hence combine the knowledge of python arrays and list for array initialization and operations.
NumPy Installation
We can install Python NumPy by going to the command prompt and typing a simple command pip install NumPy. Then go to the IDE and use the import command import NumPy as np.
We can now access all the functionalities of the NumPy module.
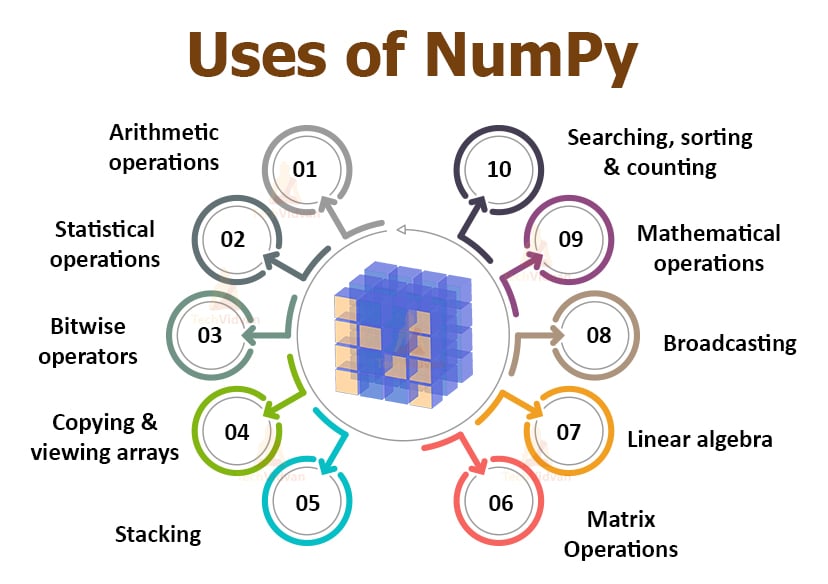
Uses of NumPy
NumPy is one of the most useful external libraries available in Python. It has a wide variety of functions to work with arrays and a powerful multi-dimensional array object. It has operations that are applicable to a vast range of platforms.
Numpy can be put to use for storing, manipulation, and deletion of array elements. We can use it for sorting, indexing, and stacking of the array elements. It has modules regarding various operations:
- Arithmetic operations
- Statistical Operations
- Bitwise Operators
- Linear Algebra
- Copying and viewing arrays
- Stacking
- Searching, Sorting, and counting, etc.
- Mathematical Operations
- Broadcasting
- Matplotlib for graphical representations
- Matrix Operations, etc.
NumPy vs. Python arrays
The NumPy library is a great alternative to python arrays. The difference is that the NumPy arrays are homogeneous that makes it easier to work with. We can initialize the array elements in many ways, one being which is through the python lists.
The NumPy arrays are convenient as they have the following three features–
- Less Memory Requirement
- Faster Processing
- Convenience of use
Data types in NumPy
Numpy supports more data types as compared to Python. These data types are instances of dtype objects. Some of the scalar data types are given in the table below.
| Sr.No. | Data Types | Description |
| 1. | bool_ | Boolean True/False |
| 2. | int_ | Integer type |
| 3. | intc | Same as C int |
| 4. | intp | An integer used for indexing |
| 5. | int8 | Byte(-128 to 127) |
| 6. | int16 | Integer(-32768 to 32767) |
| 7. | int32 | Integer(-2147483648 to 2147483647) |
| 8. | int64 | Integer (-9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807) |
| 9. | uint8 | Unsigned integer(0 to 225) |
| 10. | unit16 | Unsigned integer(0 to 65535) |
| 11. | unit32 | Unsigned Integer(0 to 4294967295) |
| 12. | unit64 | Unsigned Integer(0 to 18446744073709551615) |
| 13. | float_ | Shorthand for float64 |
| 14. | float16 | Half precision float |
| 15. | float32 | Single precision float |
| 16. | float64 | Double precision float |
| 17. | complex_ | Shorthand for comples128 |
| 18. | complex64 | Two 32bit float complex number |
| 19. | complex128 | Two 64 bit float complex number |
NumPy Operations
NumPy consists of a wide range of functions to work with arrays.
1. Numpy ndim
It is the function which determines the dimensions of the input array
import numpy as np a = np.array([(1,1,1),(2,2,2)]) print(a.ndim)
Output
2. Numpy itemsize()
We use this function to determine the size of the array elements.
import numpy as np a = np.array([(1,1)]) print(a.itemsize)
Output
3. Numpy dtype()
We use this function to determine the data type of the array elements.
import numpy as np a = np.array([(1,1)]) print(a.dtype)
Output
4. Numpy reshape()
We use this function to reassign the array a new shape.
import numpy as np a = np.array([(1,1,1),(2,2,2)]) print(a) a=a.reshape(3,2) print(a)
Output
[2 2 2]]
[[1 1]
[1 2]
[2 2]]
5. Numpy slicing()
It is for extracting a particular set of elements from the array.
import numpy as np a=np.array([(1,1),(2,2),(3,3)]) print(a[0:2,1])
Output
6. Numpy linspace()
This is for array generation of evenly spread elements.
import numpy as np a=np.linspace(1,5,10) print(a)
Output
3.66666667 4.11111111 4.55555556 5. ]
7. Numpy min() / Numpy max()
We can find the minimum and maximum values from the array.
import numpy as np arr= np.array([10,20,30]) print(arr.min()) print(arr.max())
Output
30
8. Numpy sum()
This is to return the sum of all the array elements
import numpy as np arr= np.array([10,50,100]) print(arr.sum())
Output
9. Numpy sqrt()/ Numpy std()
We can determine the square root and standard deviation of the array elements.
import numpy as np a=np.array([(1,2,3),(4,5,6)]) print(np.sqrt(a)) print(np.std(a))
Output
[2. 2.23606798 2.44948974]]
1.707825127659933
10. +,-,/, *
We can determine the sum, difference, division, and multiplication of the array elements with the use of these operators.
import numpy as np x= np.array([(1,1,1),(2,2,2)]) y= np.array([(3,3,3),(4,4,4)]) print(x+y) print(x-y) print(x*y) print(x/y)
Output
[6 6 6]]
[[-2 -2 -2]
[-2 -2 -2]]
[[3 3 3]
[8 8 8]]
[[0.33333333 0.33333333 0.33333333]
[0.5 0.5 0.5 ]]
11. Numpy hstack/ Numpy vstack()
These are stacking functions, we can perform horizontal and vertical stacking of arrays.
import numpy as np x= np.array([(1,1,1),(2,2,2)]) y= np.array([(3,3,3),(4,4,4)]) print(np.vstack((x,y))) print(np.hstack((x,y)))
Output
[2 2 2]
[3 3 3]
[4 4 4]]
[[1 1 1 3 3 3]
[2 2 2 4 4 4]]
12. Numpy ravel()
This function concerts the entire array into a single column.
import numpy as np arr= np.array([(1,1,1),(2,2,2)]) print(arr.ravel())
Output
There are a few special functions available in NumPy. We can plot the sine, cos, and tan curves using the matplotlib module. It is an alternative to other plotting software like MatLab.
It is a great alternative when working with graphical representations.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt arr1= np.arange(0,2*np.pi,0.5) arr2=np.sin(arr1) arr3=np.cos(arr1) arr4=np.tan(arr1) plt.plot(arr1,arr2) plt.plot(arr1,arr3) plt.plot(arr1,arr4) plt.show()
Summary
Here we come to the end of Numpy Tutorial.
NumPy is the basic library for mathematical operations in Machine Learning. It has a vast range of functions to manipulate arrays and matrices. It is a very convenient and user-friendly library. It has made to work with an array element a much easier task.
Working with arrays has turned out to be a much faster and time-efficient process. It is very easy to install and implement.
There are many modules in NumPy that are specific to various complex functions. It can also extend functionalities by combining with other python libraries.