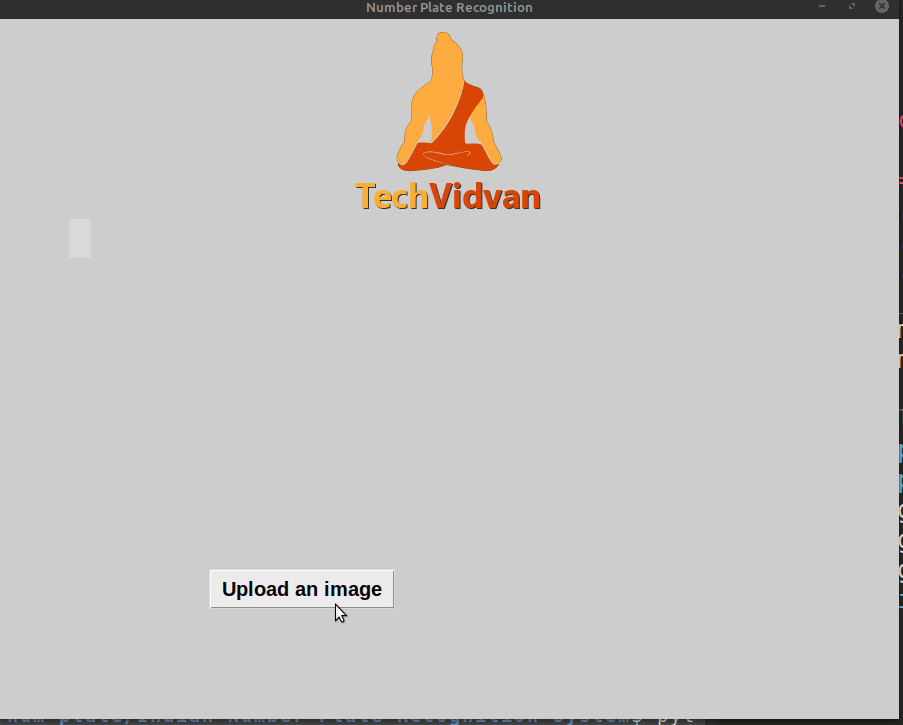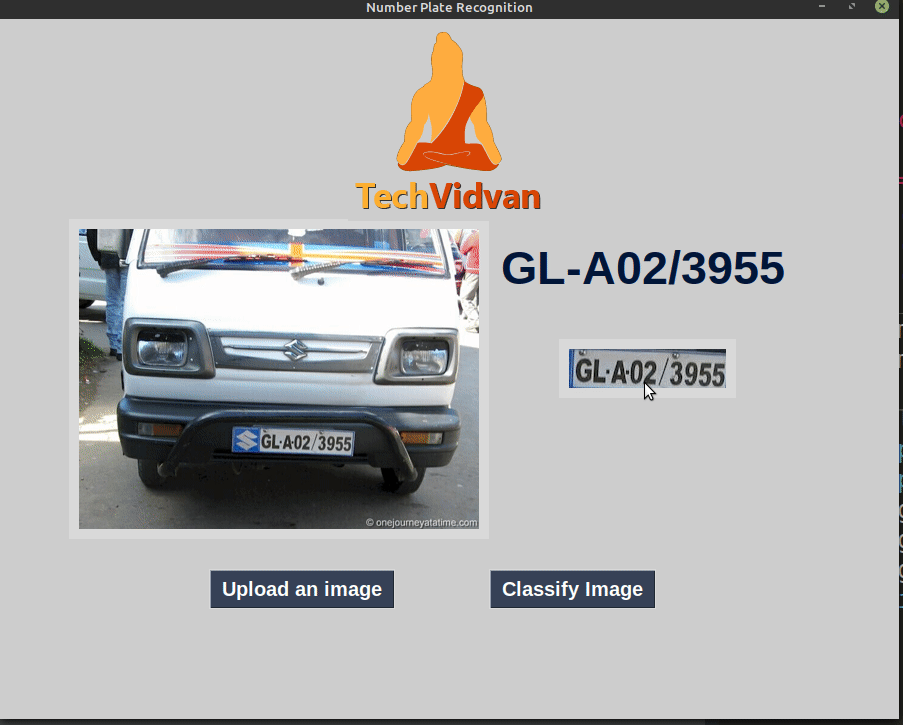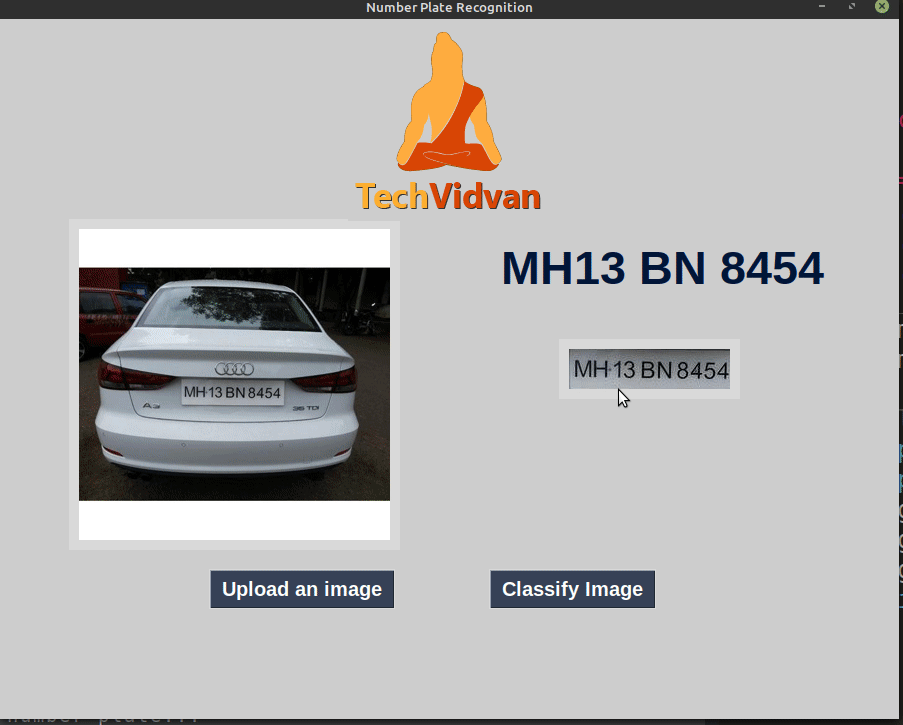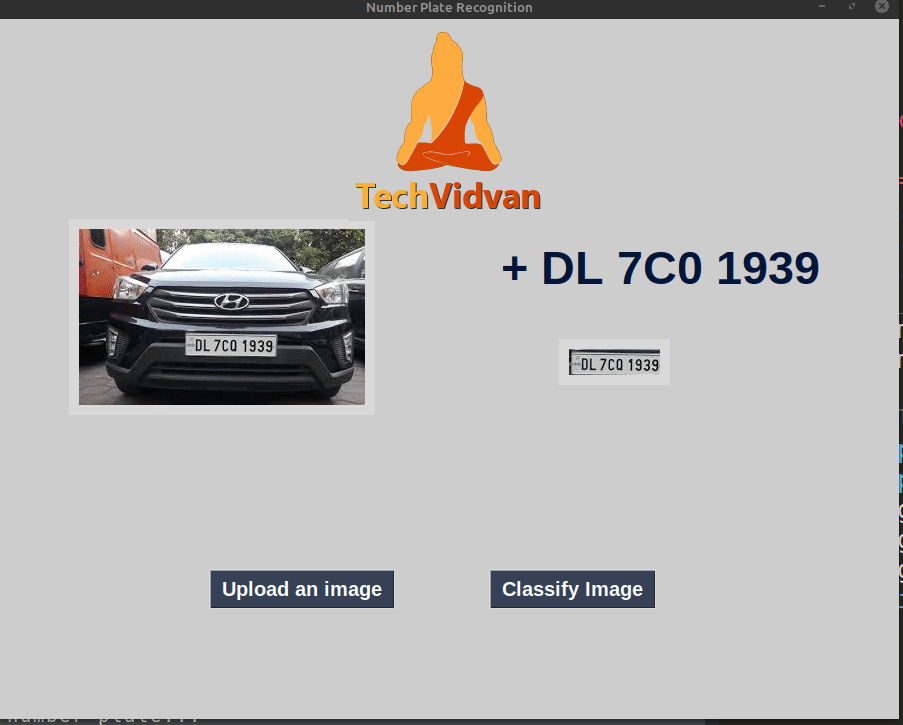
Python Project – Automatic License Number Plate Recognition using Deep Learning
Deep Learning Project – Automatic License Number Plate Detection and Recognition
This project aims to recognize license number plates. In order to detect license number plates, we will use OpenCV to identify number plates and python pytesseract to extract characters and digits from the number plates.
Automatic License Number Plate Recognition
OpenCV is an open-source machine learning library and provides a common infrastructure for computer vision. Whereas Pytesseract is a Tesseract-OCR Engine to read image types and extract the information present in the image.
Install OpenCV and Pytesseract pip3 python package:
pip3 install opencv-python pip3 install pytesseract
In this python project, to identify the number plate in the input image, we will use following features of openCV:
- Gaussian Blur: Here we use a Gaussian kernel to smoothen the image. This technique is highly effective to remove Gaussian noise. OpenCV provides a cv2.GaussianBlur() function for this task.
- Sobel: Here we calculate the derivatives from the image. This feature is important for many computer vision tasks. Using derivatives we calculate the gradients, and a high change in gradient indicates a major change in the image. OpenCV provides a cv2.Sobel() function to calculate Sobel operators.
- Morphological Transformation: These are the operations based on image shapes and are performed on binary images. The basic morphological operations are Erosion, Dilation, Opening, Closing. The different functions provided in OpenCV are:
- cv2.erode()
- cv2.dilate()
- cv2.morphologyEx()
- Contours: Contours are the curves containing all the continuous points of same intensity. These are very useful tools for object recognition. OpenCV provides cv2.findContours() functions for this feature.
Download the project source code
Before proceeding ahead, please download the source code: Automatic Number Plate Recognition
Now, let’s dive into the number plate recognition code. Follow the steps below:
1. Imports:
For this project we need numpy and pillow python libraries with openCV and pytesseract
import numpy as np import cv2 from PIL import Image import pytesseract as tess
2. Now we will define three functions, to find the unnecessary contours that openCV may identify but it does not have probability of being a number plate.
2.1. The first function to check the area range and width-height ratio:
def ratioCheck(area, width, height):
ratio = float(width) / float(height)
if ratio < 1:
ratio = 1 / ratio
if (area < 1063.62 or area > 73862.5) or (ratio < 3 or ratio > 6):
return False
return True
2.2. The second function to check average of image matrix:
def isMaxWhite(plate):
avg = np.mean(plate)
if(avg>=115):
return True
else:
return False
2.3. The third function to check the rotation of contours:
def ratio_and_rotation(rect):
(x, y), (width, height), rect_angle = rect
if(width>height):
angle = -rect_angle
else:
angle = 90 + rect_angle
if angle>15:
return False
if height == 0 or width == 0:
return False
area = height*width
if not ratioCheck(area,width,height):
return False
else:
return True
3. Now we will write a function to clean the identified number plate for preprocessing before feeding to pytesseract:
def clean2_plate(plate):
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(plate, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray_img, 110, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
if cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff == ord('q'):
pass
num_contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(),cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
if num_contours:
contour_area = [cv2.contourArea(c) for c in num_contours]
max_cntr_index = np.argmax(contour_area)
max_cnt = num_contours[max_cntr_index]
max_cntArea = contour_area[max_cntr_index]
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(max_cnt)
if not ratioCheck(max_cntArea,w,h):
return plate,None
final_img = thresh[y:y+h, x:x+w]
return final_img,[x,y,w,h]
else:
return plate, None
4. In this step, we will take an image input. We will perform Gaussian Blur, Sobel and morphological operations. After we find contours in the image and loop through each contour to identify the number plate. We will then clean the image contour and feed it to pytesseract to recognize the number and characters.
img = cv2.imread("testData/sample15.jpg")
print("Number input image...",)
cv2.imshow("input",img)
if cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff == ord('q'):
pass
img2 = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (3,3), 0)
img2 = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img2 = cv2.Sobel(img2,cv2.CV_8U,1,0,ksize=3)
_,img2 = cv2.threshold(img2,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
element = cv2.getStructuringElement(shape=cv2.MORPH_RECT, ksize=(17, 3))
morph_img_threshold = img2.copy()
cv2.morphologyEx(src=img2, op=cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel=element, dst=morph_img_threshold)
num_contours, hierarchy= cv2.findContours(morph_img_threshold,mode=cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,method=cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
cv2.drawContours(img2, num_contours, -1, (0,255,0), 1)
for i,cnt in enumerate(num_contours):
min_rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt)
if ratio_and_rotation(min_rect):
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
plate_img = img[y:y+h,x:x+w]
print("Number identified number plate...")
cv2.imshow("num plate image",plate_img)
if cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff == ord('q'):
pass
if(isMaxWhite(plate_img)):
clean_plate, rect = clean2_plate(plate_img)
if rect:
fg=0
x1,y1,w1,h1 = rect
x,y,w,h = x+x1,y+y1,w1,h1
# cv2.imwrite("clena.png",clean_plate)
plate_im = Image.fromarray(clean_plate)
text = tess.image_to_string(plate_im, lang='eng')
print("Number Detected Plate Text : ",text)
Code for Project GUI
Make a new file gui.py and paste the below code:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
from tkinter import *
from PIL import ImageTk, Image
from tkinter import PhotoImage
import numpy as np
import cv2
import pytesseract as tess
def clean2_plate(plate):
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(plate, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray_img, 110, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
num_contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(),cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
if num_contours:
contour_area = [cv2.contourArea(c) for c in num_contours]
max_cntr_index = np.argmax(contour_area)
max_cnt = num_contours[max_cntr_index]
max_cntArea = contour_area[max_cntr_index]
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(max_cnt)
if not ratioCheck(max_cntArea,w,h):
return plate,None
final_img = thresh[y:y+h, x:x+w]
return final_img,[x,y,w,h]
else:
return plate,None
def ratioCheck(area, width, height):
ratio = float(width) / float(height)
if ratio < 1:
ratio = 1 / ratio
if (area < 1063.62 or area > 73862.5) or (ratio < 3 or ratio > 6):
return False
return True
def isMaxWhite(plate):
avg = np.mean(plate)
if(avg>=115):
return True
else:
return False
def ratio_and_rotation(rect):
(x, y), (width, height), rect_angle = rect
if(width>height):
angle = -rect_angle
else:
angle = 90 + rect_angle
if angle>15:
return False
if height == 0 or width == 0:
return False
area = height*width
if not ratioCheck(area,width,height):
return False
else:
return True
top=tk.Tk()
top.geometry('900x700')
top.title('Number Plate Recognition')
top.iconphoto(True, PhotoImage(file="/home/shivam/Dataflair/Keras Projects_CIFAR/GUI/logo.png"))
img = ImageTk.PhotoImage(Image.open("logo.png"))
top.configure(background='#CDCDCD')
label=Label(top,background='#CDCDCD', font=('arial',35,'bold'))
# label.grid(row=0,column=1)
sign_image = Label(top,bd=10)
plate_image=Label(top,bd=10)
def classify(file_path):
res_text=[0]
res_img=[0]
img = cv2.imread(file_path)
img2 = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (3,3), 0)
img2 = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img2 = cv2.Sobel(img2,cv2.CV_8U,1,0,ksize=3)
_,img2 = cv2.threshold(img2,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
element = cv2.getStructuringElement(shape=cv2.MORPH_RECT, ksize=(17, 3))
morph_img_threshold = img2.copy()
cv2.morphologyEx(src=img2, op=cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel=element, dst=morph_img_threshold)
num_contours, hierarchy= cv2.findContours(morph_img_threshold,mode=cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,method=cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
cv2.drawContours(img2, num_contours, -1, (0,255,0), 1)
for i,cnt in enumerate(num_contours):
min_rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt)
if ratio_and_rotation(min_rect):
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
plate_img = img[y:y+h,x:x+w]
print("Number identified number plate...")
res_img[0]=plate_img
cv2.imwrite("result.png",plate_img)
if(isMaxWhite(plate_img)):
clean_plate, rect = clean2_plate(plate_img)
if rect:
fg=0
x1,y1,w1,h1 = rect
x,y,w,h = x+x1,y+y1,w1,h1
plate_im = Image.fromarray(clean_plate)
text = tess.image_to_string(plate_im, lang='eng')
res_text[0]=text
if text:
break
label.configure(foreground='#011638', text=res_text[0])
uploaded=Image.open("result.png")
im=ImageTk.PhotoImage(uploaded)
plate_image.configure(image=im)
plate_image.image=im
plate_image.pack()
plate_image.place(x=560,y=320)
def show_classify_button(file_path):
classify_b=Button(top,text="Classify Image",command=lambda: classify(file_path),padx=10,pady=5)
classify_b.configure(background='#364156', foreground='white',font=('arial',15,'bold'))
classify_b.place(x=490,y=550)
def upload_image():
try:
file_path=filedialog.askopenfilename()
uploaded=Image.open(file_path)
uploaded.thumbnail(((top.winfo_width()/2.25),(top.winfo_height()/2.25)))
im=ImageTk.PhotoImage(uploaded)
sign_image.configure(image=im)
sign_image.image=im
label.configure(text='')
show_classify_button(file_path)
except:
pass
upload=Button(top,text="Upload an image",command=upload_image,padx=10,pady=5)
upload.configure(background='#364156', foreground='white',font=('arial',15,'bold'))
upload.pack()
upload.place(x=210,y=550)
sign_image.pack()
sign_image.place(x=70,y=200)
label.pack()
label.place(x=500,y=220)
heading = Label(top,image=img)
heading.configure(background='#CDCDCD',foreground='#364156')
heading.pack()
top.mainloop()
Summary
In this article, we have developed a deep learning project to recognize license number plate. We discussed some important features of openCV like Gaussian blur, Sobel operators, Morphological transformations. The application detects number plate text from an image. We have identified and cleaned the number plate using openCV. To identify the number plate digits and characters we used pytesseract.