Android Architecture and Components
In this article, you will study Android Architecture. Any android developer must know Android Architecture in depth. This article will clearly explain what android architecture is and the five components that make up android architecture.
What is Android?
Android is an open-source operating system widely used in mobile, smartphones, and tablets. Android is based on top of the Linux kernel(modified version). As Android is open-source, anyone can download its source code, edit it according to his requirements, and launch his own custom ROM.
Android Architecture
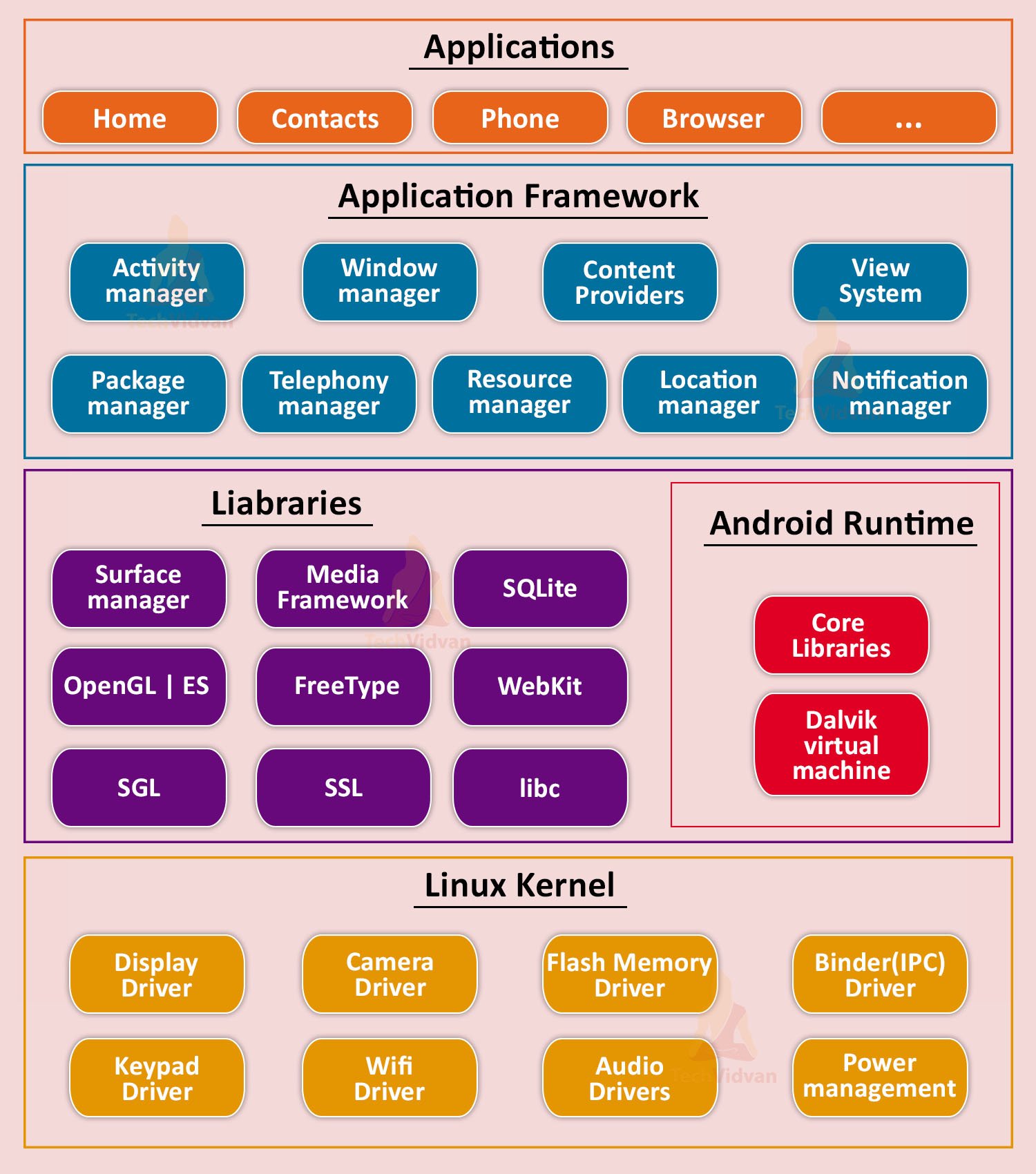
Any Operating System has its architecture to carry on various functionalities. Similarly, android has its architecture. The android architecture gives us an idea about its design and the build. The architecture can be subdivided into five broad categories:
1. Linux Kernel
Linux Kernel is the bottom-most layer of the architecture. It carries all the drivers for the low-level devices like Binder (IPC) Driver, Power Management, Audio Driver, Wi-Fi Driver, Keyboard Driver, etc.
For example, whenever you press your phone’s power button, the phone comes into the wake-up state, and this happens because the power management driver is installed. Similarly, whenever you want to capture a picture, you can because of the Camera Driver installed on the Linux kernel.
It is also known as the abstract layer of android. This is because it helps us communicate between various hardware components and interact with the upper layers of android architecture.
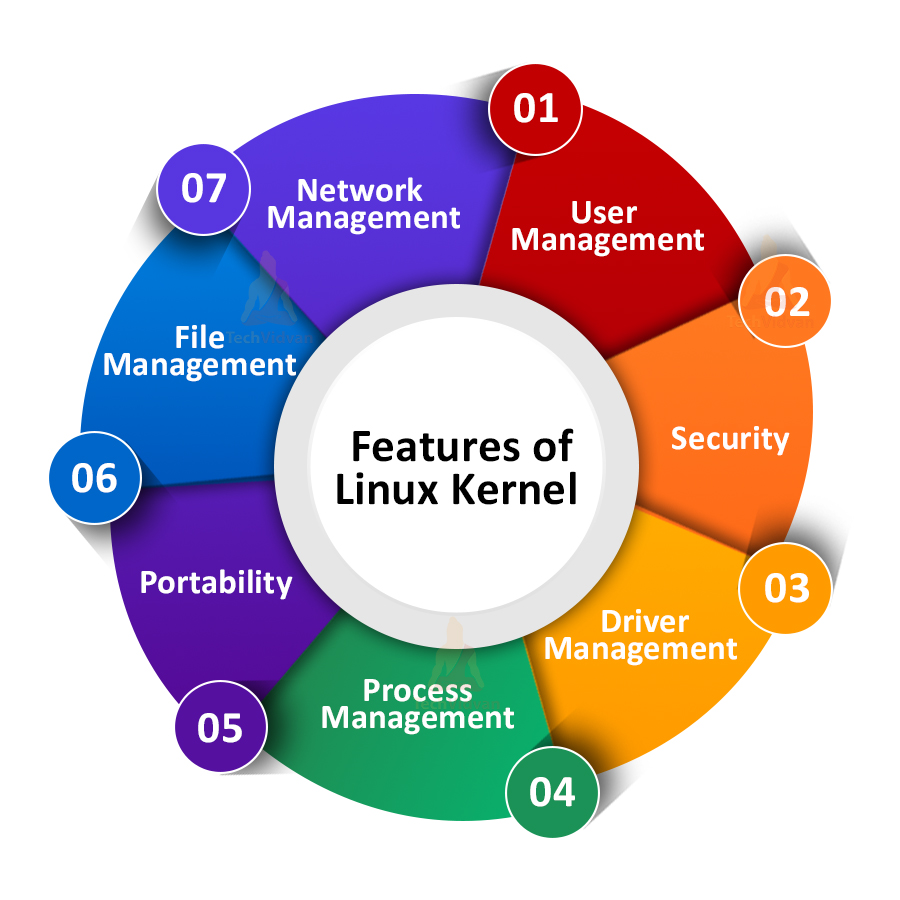
Following are some of the features of Linux Kernel:
a. Network Management
It allows networking support and routes networks, and looks into the network stack.
b. User Management
Linux handles various types of user authentication and allows users to interact with the device.
c. Process Management
It handles all the processes and decides when to start/pause or stop them.
d. File Management
It manages the memory and file systems and allows user data storage and access.
e. Driver Management
The Linux kernel manages all the drivers of the respective hardware. It helps us to interact with the hardware of our device.
f. Security
As Linux authenticates users before giving them access, it also looks for safety and maintains that other users can’t access or manipulate your data.
g. Portability
As various devices support Linux, it allows several devices to share resources and data. Almost all hardware components can interact with Linux.
2. Libraries
There are several libraries to provide various functionality for purposes like android development. These libraries are written in C/C++ and are an essential part of the android architecture.
Some of the libraries which are present in the Android architecture are as follows:
a. Surface Manager
Whatever you see on the screen, whether it’s buttons, app icons, or any layouts, is displayed with the help of the surface manager. The surface manager binds these kinds of stuff and forms a binary image displayed by the display driver.
b. Open GL ES
Open GL Embedded system is used for any kind of 3-D graphics.
c. SGL
Scalable graphics library (or SGL) is used for any kind of 2-D graphics.
Media Framework: It helps us processing videos of various video Codecs. For example, H. 264, MPEG-4, AVI, etc.
d. SQLite
It is a scrapped-out (or lower version) of SQL. Whatever libraries you call or whatever read/write or file operations you make are done through SQLite
e. WebKit
It helps in rendering, parsing, encrypting, or decrypting any kind of HTML data.
f. FreeType
It is a font rendering library, like how you have .ttf font files for windows. Similarly, in android, the font library helps in reading and writing text in various types of font styles and then renders it.
g. SSL
SSL (also known as secured socket layer) is used for data encryption and decryption.
h. Libc
It’s a C compiler developed by google to perform all low-level compilations.
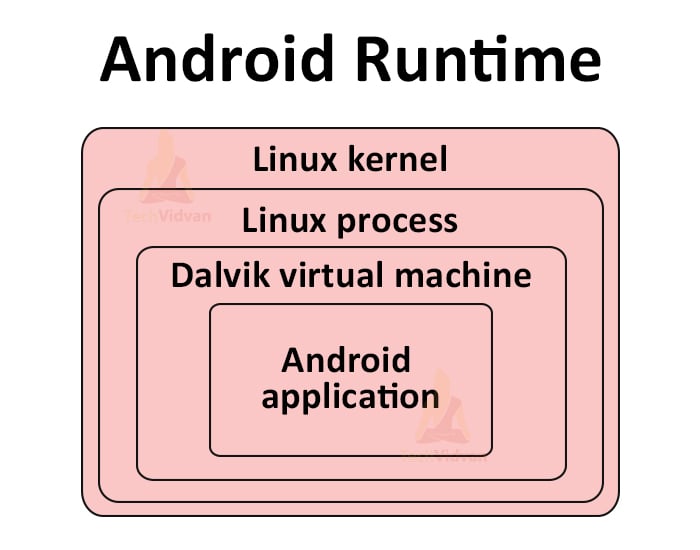
3. Android Runtime
It provides us an environment for executing and debugging our android applications. This is implemented either through Dalvik Virtual Machine or ART.
Before Android KitKat, you tend to use Dalvik Virtual Machine, but the most recent Android versions now prefer using ART. Along with this, it also has some core libraries which are written in Java.
For example, in Java, you have JVM, which converts the byte code to machine code. Similarly, in Android, you have DVM or ART, which converts the byte code to a .dex file.
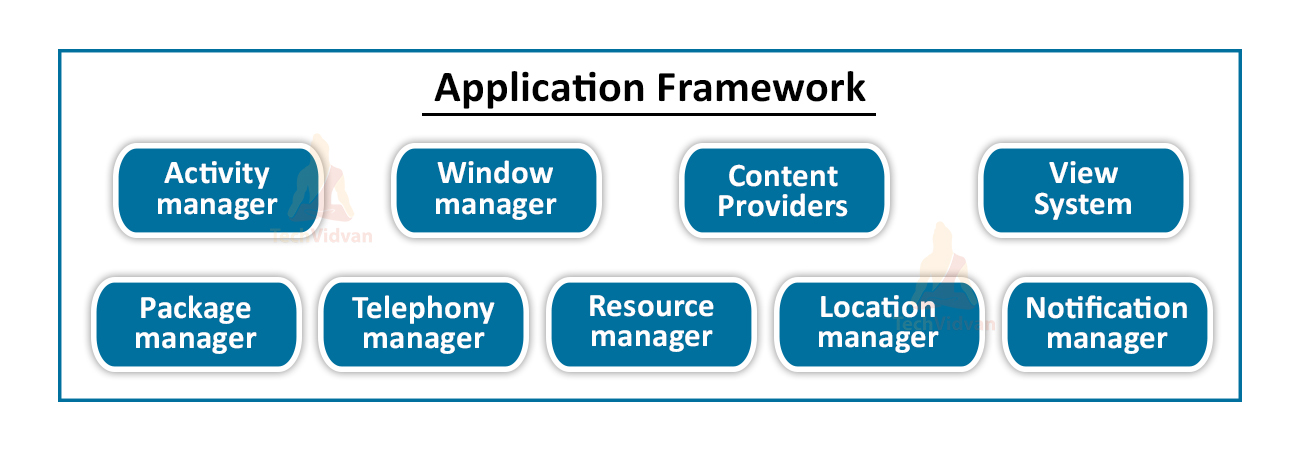
4. Application Framework
It has many packages in it which are implemented in Java. Some of them are as follows:
a. Activity Manager
Activity is nothing but the visible component through which the User interacts with his application.
Suppose you are chatting with your friend on WhatsApp, so you are using the WhatsApp activity, but suddenly if you press the home button, then you will come to the Home screen of your Smartphone. These all things, including multitasking, are managed through the activity manager.
b. Content Provider
It helps us seek permission from users to do various tasks, like accessing the camera, gallery, or accessing data from other applications.
c. Telephony Manager
It helps in managing phone calls and keeping logs of that calls.
d. Notification Manager
It notifies users about the activities or processes running in the background or foreground.
Similarly, there are many such components as Package Manager, Location Manager, Resource Manager, View System, etc., having individual use.
5. Applications
At the top level of the architecture, you have the applications. Applications can be of system or user or even kept by the OEM manufacturers. Phone, Messaging, Camera, Gallery, Settings, etc., are typical applications present in any android device.
Summary
So from this article, you saw what is android architecture and why it is imperative for any android developer to know about it. You understood all the five components present in the architecture and their features, benefits, and examples. This knowledge of Android Architecture will further help you to know how any android application works in a better manner,