Big Data Security – Implementation, Use cases and Issues
Today the adoption of Big data analytics is rapidly growing in each sector. If you plan ahead in Big data, then there are big opportunities to successfully enable your business.
But the challenge is that big data analytics platforms are usually filled by a huge volume of products, partners, customers, and other data. This data generally has insufficient data security which acts as a great opportunity for cybercriminals.
What is Data Security?
Big data security can be termed as the tool and measures which are used to guard both data and analytics processes.
The main purpose of Big data security is to provide protection against attacks, thefts, and other malicious activities that could harm valuable data.
Big data security challenges are multi-faced for the companies that operate on the cloud. This challenging threat includes the theft of information stored online, ransomware, or DDoS attacks that could crash a server.
These threats can cause serious financial repercussions such as losses, litigation costs, and fines or sanctions of an organization.
Sensitivities around Big data security and privacy are a hurdle that needs to be overcome. Intelligent analytics has been introduced to enhance security with the help of the proposed security intelligence model.
How you can implement Big Data Security in Organizations?
Encryption is one of the most common security tools. Encrypted data is hard to decode for hackers.Encrypted data is generally done for the incoming data as well as for outgoing data.
If we look at the other Big data security tools, then the best one is Firewall. Firewalls are usually used to filter the traffic that enters and leaves servers. Firewall creates strong filters that prevent attacks from malicious activities.
BI tools and analytics platform is another key to protect vital information of the organization. BI tools used to create an access system that can reduce the possibility of an attack to a great extent.
Some of the reasons why it is important to follow the best practices for Big Data security are mentioned below :
- It boosts the security of non-relational data scores.
- It helps to implement endpoint security.
- Ensures the safety of transactions and data storage logs.
- Rely on Big Data Cryptography.
- Use Customized solutions.
- Practice real-time security monitoring and compliance.
- Enhances communication and availability of information.
- Allows for convenient resource sharing.
- Increases systems efficiency and robustness.
- Avoiding unauthorized access thus protects and enhances the performance and security of the organization.
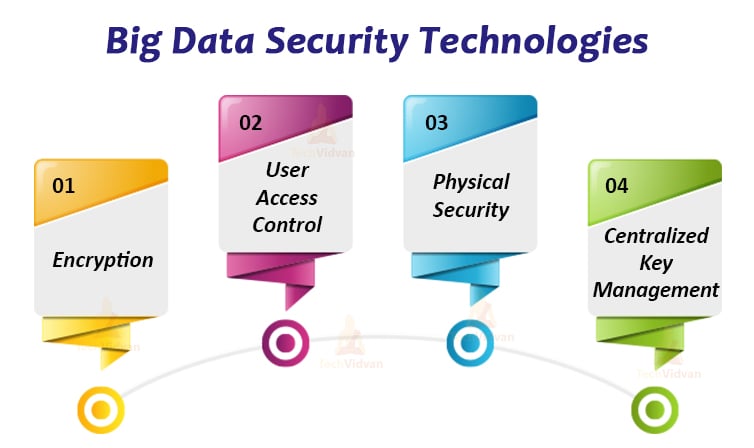
Big Data Security Technologies
1. Encryption
Encryption of data is generally done to secure a massive volume of data, different types of data. It can be user-generated or machine-generated code. Encryption tools along with different analytics toolsets format or code the data.
They also get applied to data from different sources like relational database management system (RDBMS), specialized file systems like Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), etc.
2. User Access Control
It is the most basic network security tool. But few companies practice this because it involves high management overhead, this can be dangerous at the network level and not good for the Big data platforms.
Automated strong user access control is a must for organizations. Automation control manages complex user control levels that protects the Big data platform against the inside attack.
3. Physical Security
Physical security should not be ignored. It is generally built in when you deploy the Big data platform in your own center. It can also be built around your cloud provider’s data center security.
They are important as they can deny data center access to strangers or suspicious visitors. Video surveillance and security logs are also used for the same purpose.
4. Centralized Key Management
It is one of the best security practices for many years. It is applied in Big data environments, especially on those having wide geographical distribution.
Best practices under centralized key management include policy-driven automation, on-demand key delivery, logging, and abstracting key management from key usage.
Some of the companies practicing Big Data Securities are:
Below are a few of the representatives of Big data security companies.
1. Cloudwick: CDAP (Cloudwick Data Analytics Platform) is a managed security hub that integrates security features from multiple analytics toolsets, traditional IDS and IPS, and machine learning projects. CDAP builds on Intel Xeon and Cloudera’s Hadoop distribution.
2. IBM: IBM security Guardium is used to monitor Big data and NoSQL environments. It includes the discovery and classification of sensitive data.
Vulnerability assessment, and data and file monitoring is also done under IBM security. Guardium monitoring also masks, blocks, alerts, encrypts and quarantines the suspicious access attempts.
3. Logtrust: Logtrust is partnered with Panda Security in order to provide the ART (Advanced Reporting Tool) and Panda Adaptive Defense. Suspicious digital behavior and internal threats to Big data systems and networks get automatically reported by the ART.
Panda Adaptive Defense generally correlates data from multiple sources, which is critical in Big data environments with multiple nodes and data sources.
4. Gemalto: Gemalto SafeNet protects Big data platforms. Usually, it protects the Big data platforms in the cloud, data center, and virtual environments. The toolset of security includes digital signing solutions, data encryption, strong authentication, and cryptographic key security management.
Gemalto integrates with MongoDB, DataStax, IBM, Cloudera, Zettaset, Hortonworks, and Couchbase, they all are leading Big data providers.
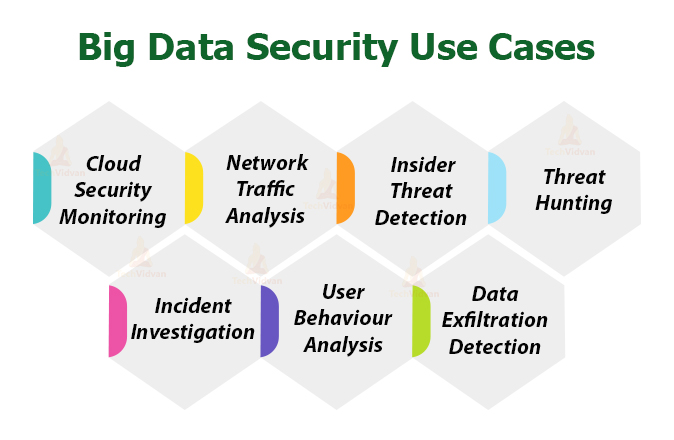
Big Data Security Use Cases
1. Cloud Security Monitoring
Cloud computing generally offers more efficient communication and increased profitability for all businesses. This communication needs to be secure.
Big data security offers cloud application monitoring. This provides host sensitive data and also monitors cloud-hosted infrastructure. Solutions also offer support across several relevant cloud platforms.
2. Network Traffic Analysis
Traffic continually moves in and out of your network. Due to the high volume of data over the network, it is difficult to maintain transactional visibility over the network traffic.
Security analytics allow your enterprise to watch over this network traffic. It is used to establish baselines and detect anomalies.
This also helps in cloud security monitoring. It is used to analyze traffic in and out of cloud infrastructure. It also illuminates dark spaces that are hidden in infrastructures and analyze encrypted sensitive data. Thus, ensuring the proper working of channels.
3. Insider Threat Detection
Insider threats are as much as a danger to your enterprise as external threats. An active malicious user can do as much damage as any malware attack. But it is only in some rare cases that an insider threat can destroy a network.
With the help of security analytics, organizations can easily detect the insider threats. This is anticipated through behaviors such as abnormal login times, unusual email usage, and unauthorized database access requests.
Sometimes it also looks for indicators that ask for visibility to third-party actors.
4. Threat Hunting
Generally, the IT Security team mostly engage in threat hunting. They search for potential indicators of dwelling threats and breaches that try to attack the IT infrastructure.
Security analytics helps to automate this threat of hunting. It acts as an extra set of eyes for your threat hunting efforts. Threats hunting automation can help in detecting malware beaconing activity and thus alerts for its stoppage as soon as possible.
5. Incident Investigation
Generally, the sheer number of security alerts from SIEM solutions would overwhelm your IT security team. These continuous alerts can cause more fostering burnout and frustration.
Thus to minimize this issue, security analytics automates the incident investigation by providing contextualization to alerts. Thus your team has more time to prioritize incidents and can deal with potential breach incidents first.
6. User Behaviour Analysis
Organization’s users generally interact with your IT infrastructure all the time. Mainly it is the user’s behavior that decides the success or failure of your cybersecurity. Therefore there is a need for tracking user’s behavior.
The security analytics monitor the unusual behavior of employees. Thus it helps to detect an insider threat or a malicious account. It can also detect suspicious patterns by correlating malicious activities.
An example of one such renowned security analytics use case is UEBA. It helps to provide visibility into the IT environment. Thus compiling user activities from multiple datasets into complete profiles.
7. Data Exfiltration Detection
Data exfiltration is termed as any unauthorized movement of data moving in and out of any network. Unauthorized data movements can cause theft and leakage of data.
Thus there is a need to protect data from such unauthorized access. Security analytics helps to detect the data exfiltration over a network. It is generally used to detect data leakage in encrypted communications.
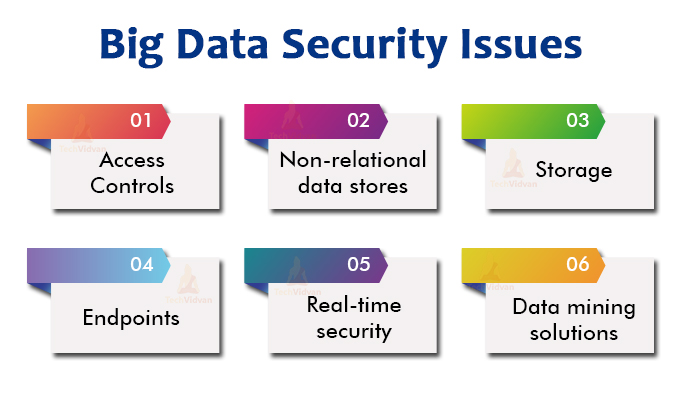
Big Data security issues
- Access Controls: It is critically important for an organization to have a system which is fully secure.Permission to exchange the data should be permitted to authenticated users only. Access control needs to be such that it would not get hacked by attackers, hackers, or by any malicious activities. But to build a fully secure and strong access control is a big issue for organizations as it involves a big investment and a lot of maintenance.
- Non-relational data stores: Non-relational databases like NoSQL usually lack security by themselves.
- Storage: In Big data architecture, we store data on multiple tiers. Its storage depends on business needs in terms of performance and cost. For example, high-priority data is generally stored on flash media. So locking down storage means creating a tier-conscious strategy.
- Endpoints: Security solutions that usually draw logs from endpoints will need to validate the authenticity of those endpoints or the analysis is not going to do much.
- Real-time security/ compliance tools: Real-time tools generally generate a large amount of information. The key is to find a way to ignore false or rough information. So that human talent can be focused on true breaches or valuable information.
- Data mining solutions: Data mining solutions generally find a pattern that suggests business strategies. For this reason, there is a need for ensuring that it is secured from both internal and external threats.
Also there are some of the typical challenges in Securing Big Data:
- It is difficult for security softwares to protect new toolsets or new technologies like Advanced analytic tools for unstructured Big data and non-relational databases like NoSQL.
- Security tools are very efficient and effective to protect data storage. But they do not have the same impact on data output from multiple analytical tools to multiple locations.
- Big data administrators generally mine the data without permission or notification. But whether the motivation is curiosity or criminal profit, security tools need to monitor only on suspicious access.
- The size of Big data installation is in terabytes to petabytes which are too big to handle. And most Big data platforms are cluster-based, due to which there are multiple vulnerabilities across multiple nodes and servers.
- If there is no regular update of security done by a Big data owner then there is risk of data loss and exposure.
- Big data security experts need to continuously update their knowledge regarding cleanup and removal of malware and threats.
Conclusion
There are several challenges in securing Big data. So when you are hosting the Big data platform in the cloud, try to take nothing for granted. There is a need to work closely with the service provider to overcome these challenges with strong security SLA (Service Level Agreement).
Who is responsible for the security of this vital Information ??? Everyone….yes almost everyone working in an organization is responsible for securing the important data.
IT is responsible for policies and procedures, and security software. Software security helps to protect Big data deployment against malware and unauthorized access.
Compliance officers must work with the IT team closely to protect compliance, which means protecting the automatic stripping credit card numbers. To safeguard the databases DBA (Database Administrators) should also work closely with the IT team.
Securing the Big data platform from high and low threats will allow your organization to provide services well in the long run.
Hope you liked the article. Do share feedback in the comment section.