Android Web Services
In this article, we will cover web services in android. Web services are quite essential while dealing with any applications. Most of the applications running these days use web services. Web services, in simple terms, mean providing service over the web.
In other words, web services make your application capable of communicating to the server or other applications. With the help of web services, your application gets an edge to access and send data over the internet.
From this article, you will understand what web services are and understand the several protocols used to communicate between systems or applications.
What are Android Web Services?
Android Web Services is a standardised system that helps various applications and systems to communicate with each other. While communicating, they can exchange information and also share some services among themselves. Android web services can run on the internet or private local networks depending on the requirements. Android Web Services are pretty helpful in establishing connections and ensuring security while sharing data in the network.
Below is a ubiquitous example of android web services, which would help you understand the android web services. Suppose your application can seek restaurant data from the server and then display it in your application. The application can then send back the desired list of items to the server, and then the admins can fulfil your order.
So, you can notice that data has to flow from server to application and from application back to the server. In such scenarios, Android Web Services play a significant role in establishing and deciding the protocols for communication.
How do Web Servers work?
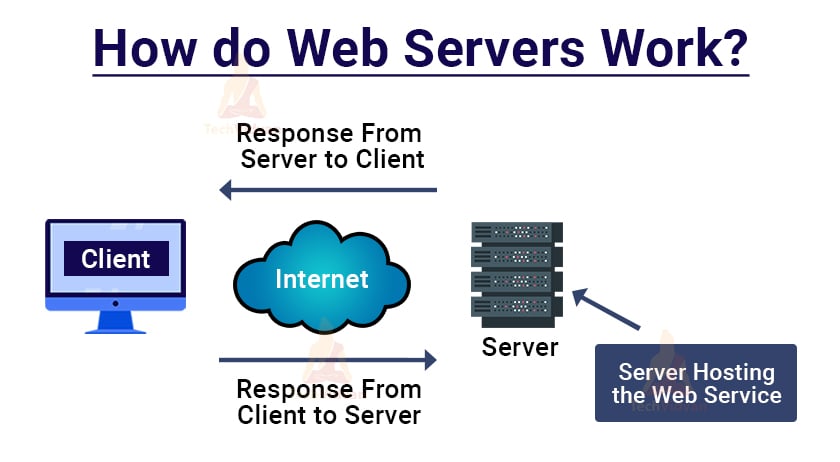
When we consider web services, there are two essential parts of a web service known as client and server.
Client: The client is the user or the requesting application that requests data or information from a server.
Server: Server is like an admin who responds to client’s requests. Servers can handle more than one client and decide whether to fulfil or decline client requests. The server is the place where our web service is hosted globally or locally.
The below figure describes how web servers work and how client and server interact.
Components of Android Web Services
Now, let’s see some of the components present in the web server and understand their role.
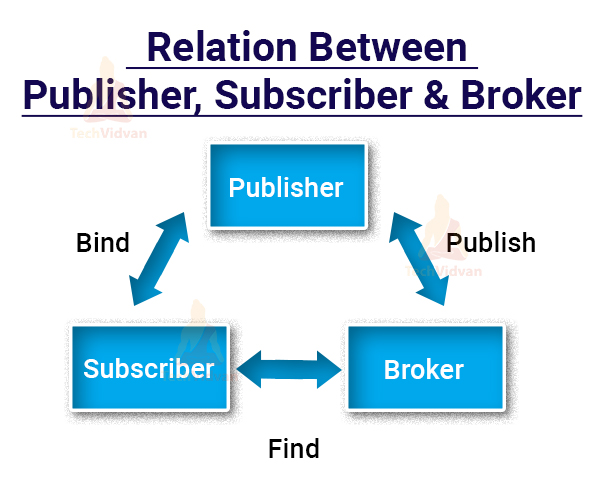
1. Publisher – Publisher provides web services to clients and is also known as a service provider.
2. Subscriber – The subscriber is the user or the application that requests services from the publisher.
3. Broker – Usually, the Subscriber is unknown about the publisher and needs something to guide the location of the web service. So, the broker is the application that helps the subscriber to identify the web service. The broker gives the subscriber access to UDDI(User descriptive, discovery, and integration).
Now, let’s see the roles and operations each of them carries out.
- Publish – Publish means creating the web service and describing its location to the broker for its easy identification by subscribers.
- Subscribe – Subscribe means that the subscriber locates the web service with the help of the broker.
- Bind – After the subscriber successfully fetches the location, the subscriber binds itself with the web service to exchange information.
Characteristics of Web Services in Android
I hope until now you are clear with what web services are and the components involved in them. Now, it’s time for us to look at some of the web services in android.
a. Web Services are XML-Based – Both client and server use XML as their communication language. In other words, the client requests in XML and receives a response, which is XML.
b. Web services are not tied to one specific operating system or programming language. For example, a Java-based application can communicate with a Perl based application.
c. Web Services are available on both the internet or on the local network.
d. Web Services are not tightly coupled. In other words, the client-side web service and the provider side web service are not directly tied.
e. Web Services can be either synchronous or asynchronous. By being synchronous, the clients can directly perform functionalities without establishing a connection. By being asynchronous, the client first needs to establish a connection and then perform the functionalities.
f. Web Services allow you to share multiple files, including documents and complex ones.
XML Remote Procedure Calls (RPC)
One of the best ways to communicate documents and information across computers is through remote procedure calls. Let’s look at some XML-RPC details:
1. It does Remote Calls using XML messages.
2. These queries are sent over HTTP POST and are encoded in XML.
3. XML responses are integrated similarly to HTTP responses.
4. XML- RPC is platform-agnostic as well as language-agnostic.
5. It enables several apps to communicate with one another.
6. It was created in accordance with W3C guidelines.
Types of Web Services in Android
There are four types of Web Services available in android and are listed below:
1. XML-RPC
XML-RPC, popularly known as Remote Procedure Calls, are used to exchange information among large devices. Every call is encoded using XML, and HTTP is used for its transmission.
2. UDDI
UDDI is an acronym for Universal Descriptive, Discovery, and Integration. It is an XML-based standard that is used to describe, publish, and discover new web services.
3. SOAP
SOAP refers to the Simple Object Access Protocol and is an XML-based web service protocol for exchanging data or documents over HTTP (Hypertext transfer protocol) or SMTP (Simple Message Transfer Protocol). It allows separate processes on different platforms to communicate with one another.
4. REST
REST(REpresentational State Transfer) is an architectural pattern that allows multiple web service-based systems to interact and communicate efficiently. RESTful systems(the system in compliance with REST service) are distinguished by their statelessness and separation of client and server concerns.
Advantages of Android Web Services
1. Web services make it possible for various applications to communicate with one another.
2. Reusability is one of the essential benefits of using web services.
3. Web services allow for more efficient communication within and across applications and organisations.
4. They communicate across various apps using a high-quality industry-standard protocol.
5. They employ SOAP over HTTP to enable web services via a low-cost internet connection.
6. Web Services are made available using conventional internet protocols.
7. They enable us to make the functionalities of current programmes available to the public via the internet.
Limitations of Android Web Services
Even though web services are pretty beneficial still there are certain demerits of Web Service, which are listed below:
1. They don’t take advantage of new Web advancements.
2. Web services can’t be accessed using a browser.
3. Web services utilise the HTTP protocol, which is unreliable and unsafe.
Summary
Through this article, you came across web services and understood what it means. You came across the working and the components of web services. You saw what is meant by client and server and also saw the mode of communication they follow. Then you came across the characteristics of web services in android.
Moving further, your XML-RPC and also saw the other types of web services present in android. Finally, you came across the advantages and demerits of having a web service.
