How to Send SMS in Android?
Today, we will cover yet another exciting topic. You might be well aware of the feature of sending messages from android. Through this article, you will understand how you can send SMS to other devices using an application. For this, you need to know a few things.
Two ways to Send SMS on Android
First, SMS means short message service. So, you understand that it’s a service, and we term it as Messaging service. To send a message, you require the recipient’s phone number.
Now there are two ways to send SMS. They are as follows:
1. Using SMS Manager API
2. Using Built-in Application to send SMS.
Before going to any of the above methods, you need to add Send SMS permission in your manifest file. You can copy-paste the below in your manifest file.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS"/>
Now let’s see each of the methods along with code snippets.
SMS Manager API
SMS Manager API is used to send text, data, and PDU messages. You can implement SMS Manager API by copying the below code.
//Creating SMS Manager object val smsManager: manager = SmsManager.getDefault() //Calling sendTextMessage manager.sendTextMessage(recepient_number, null, the_message, null, null)
Built-in Application Method
So, above, you saw how you could send messages using SMS Manager API. Now, you will know how you can use your built-in SMS application to send messages. You can find the code below for this method.
val msg_uri = Uri.parse("smsto:recepient_phone_number")
val msgIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, msg_uri)
msgIntent.putExtra("message", "content of your message.")
startActivity(msgIntent)
SMS Manager Class
SMS Manager Class, as you know, is used to send messages and data. Above you saw a way how you can use the SMS manager API to send a text message. Now we will see the other methods that are present in the SMS Manager Class.
1. ArrayList<String> divideMessage()
The divide message is used to divide the long message into sub-messages within the range.
2. void sendDataMessage()
Using the sendDataMessage() method, you can send messages that contain some data in them.
3. static SmsManager getDefault()
Using the above method, you can create an object of the SmsManager class.
4. void sendTextMessage()
The sendTextMessage() method is used to send a message that consists of only text in it.
Implementation of Location-Based Services in Android.
So, after understanding the above concepts. We are ready to implement the concepts through a messaging application. The application will contain a button and two edit texts to send a message.
Follow the below steps to achieve the goal.
Step 1: Launch your Android Studio.
Step 2: Select Create a New Project.
Step 3: Select Empty Activity and proceed.
Step 4: Enter your application name. In my case, it’s “TechVidvanSendSMS” Next, select Kotlin from the dropdown. For the API level, select API 22 for now.
Step 5: Now, you need first to add the send SMS permission in your Manifest file.
Code:AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.techvidvan.techvidvansendsms">
<!-- Adding Permission to send SMS -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.TechVidvanSendSMS">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Step 6: Now go to res —> layout —-> and open activity_main.xml. Now here, you need to add two edit texts and a button.
Code: activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tech Vidvan"
android:textColor="#FF9800"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/recipient_phone_number"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="20dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:hint="Enter Recipient's Phone Number "
android:textColor="@android:color/black" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/your_message"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="20dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:hint="Please enter your message"
android:textColor="@android:color/black" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/send_your_sms"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:onClick="sendSMS"
android:text="Send Your Message" />
</LinearLayout>
Step 7: Now, just open your MainActivity file and paste the below code.
Code: MainActivity.kt
package com.techvidvan.techvidvansendsms
import android.Manifest
import android.content.pm.PackageManager
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.telephony.SmsManager
import android.text.TextUtils
import android.view.View
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.EditText
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat
import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity()
{
//declaring the variables
lateinit var button: Button
lateinit var recipient_number: EditText
lateinit var your_message: EditText
private val permissionRequest = 901
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
//binding edit text views with variable
recipient_number = findViewById(R.id.recipient_phone_number)
your_message = findViewById(R.id.your_message)
//binding button with the variable
button = findViewById(R.id.send_your_sms)
}
private fun sendMessage()
{
//fetching the number from edit text field
val number: String = recipient_number.text.toString().trim()
//fetching your message from edit text
val msg: String = your_message.text.toString().trim()
if (number == "" || msg == "")
{
//if number or message is empty
Toast.makeText(this, "Please enter all the fields", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
else
{
//if both number and message is not empty
if (TextUtils.isDigitsOnly(number))
{
//if number contains only digits
//creating sms manager object
val smsManager: SmsManager = SmsManager.getDefault()
//use sms manager api to send the message
smsManager.sendTextMessage(number, null, msg, null, null)
//if the message is sent successfully then show toast
Toast.makeText(this, "SMS Sent Successfully", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
else
{
//if number has other than digits then show wrong number
Toast.makeText(this, "Wrong Number!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
}
override fun onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode: Int, permissions: Array<out String>, grantResults:
IntArray)
{
super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults)
//checking if the permissions are granted
if (requestCode == permissionRequest) {
if (grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
sendMessage()
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "Please provide permission",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
}
fun sendSMS(view: View)
{
//when you press the button
val permissionCheck = ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, Manifest.permission.SEND_SMS)
if (permissionCheck == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
{
//if permission is granted, then send the message
sendMessage()
}
else
{
//if not granted, then seek again
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, arrayOf(Manifest.permission.SEND_SMS),
permissionRequest)
}
}
}
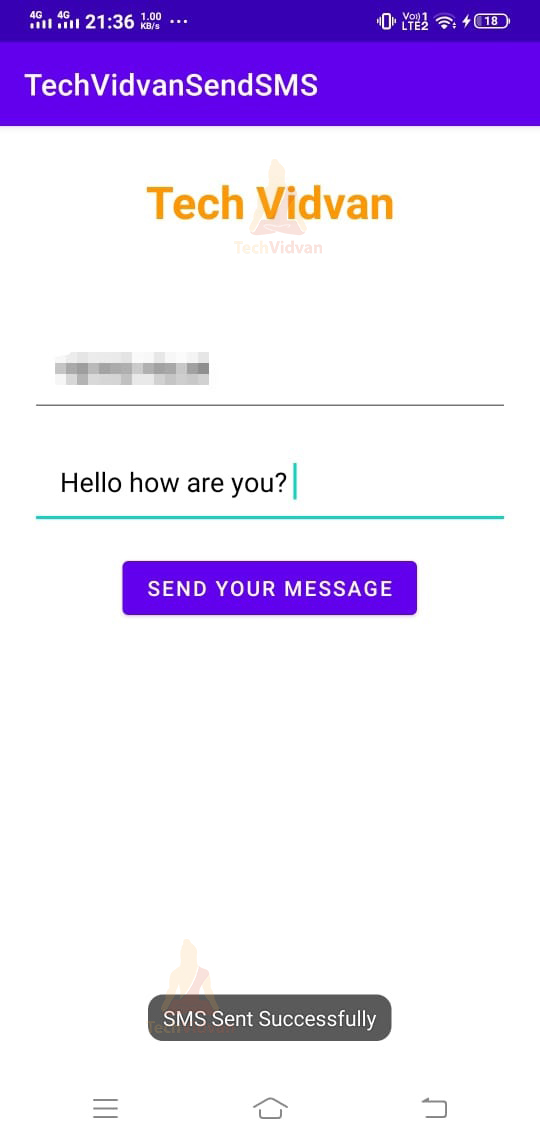
So, now your application is ready.
Summary
So through this article, you got to know about the various ways you can send SMS to other devices. You saw in detail what an SMS Manager API is and how you can use several methods. Finally, you saw a demo of creating your messaging application.