Cloud Computing Introduction
The IT industry is growing and adopting various changes and one of the latest technologies is Cloud Computing. Many users or organizations are adopting or have already adopted the Cloud. So, in the article below, we will walk about Introduction to Cloud Computing. Let’s begin.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing consists of delivering computing resources as a service. It means that the owner of the resources and the management responsibility is of the cloud provider. Clients have to pay a monthly or annual service fee to the cloud providers.
Basically, Cloud Computing is an advanced alternative solution for the on-premises data center. If the IT organization has an on-premises data center, they have to take care of the hardware cost, maintenance, installation of hardware, and software management.
But if an organization moves towards Cloud Computing, the vendor is responsible for purchasing the hardware and maintenance. These vendors will provide users with a wide range of software and platform as a service to work.
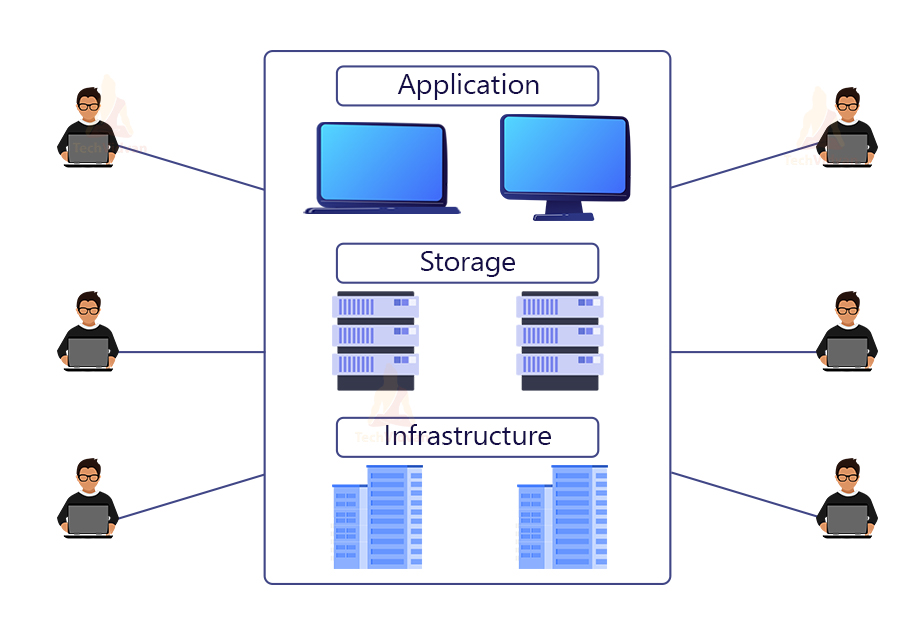
These resources charge or billing is always depending on usage, and the cloud environment will provide users an easy and accessible online portal. It helps users be comfortable and manage to compute, network, storage, and other resources.
How Cloud Computing Works?
Previously many IT companies were owning their self-computing infrastructure or data centers. But, today, most of these companies can rent access to any resources, applications, storage facility from a cloud provider.
The benefit of cloud computing services is that the companies can avoid the upfront cost of purchasing and maintaining resources. They can focus on the operational cost and simply pay for the resources which they use.
As a return, the cloud providers can benefit by delivering the same set of services to a wide range of customers.
History of Cloud Computing
The inauguration idea of cloud computing was done in 1996 inside the Compaq internal document. The term Cloud has initially been inspired by the concept of distributed computing.
In the early 1900s, Distributing Computing got accepted at Apple-spawned General Magic. The academic work and planning were performed earlier.
The concept of Cloud was first discussed with J.C.R. Licklider, the first director of the Information Processing Techniques Office at the Pentagon’s ARPA division, in 1960.
The U.S. Department of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) started to plan and develop ideas that anticipated some of the significant features of cloud computing. However, Cloud Computing was not widespread until the first decade of the 21st Century.
Popular cloud services like Amazon Elastic Cloud Compute, Simple Storage Service in 2006. In 2007 Heroku was followed by Google Cloud Platform in 2008, Alibaba Cloud in 2009, Windows Azure or Microsoft Azure in 2010.
IBM’s Smart Cloud and Digital Ocean Cloud in 2011. These services permit users to migrate their existing business to cloud resources and help independent developers create and deploy applications. The SaaS delivery model got famous in this period.
Some Cloud-based services like Gmail, Google Drive, Dropbox, and many more are offerings by companies that launched cloud infrastructure services. Today, Cloud-based infrastructure and Cloud-based applications are famous for both business and personal users.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
The Main elements of Cloud Computing are as follows:
1. On-Demand Self Service: The users can access the Cloud resources without any human interaction. In this model, the user can gain immediate access to the cloud resources by signing up. The organizations can also create policies that allow the employees to work on internal access to cloud resources.
2. Broad Network Access: The users can access cloud services with any device and by using any network location provided and permission they have.
3. Resource Pooling: The resources in the Cloud are shared with many users or multiple tenants. The data of each client is invisible from other clients.
4. Rapid Elasticity: In Cloud Computing, the resources are quickly increasing and decreasing. If compared to On-Premises hardware and software, it is a difficult task.
5. Measured Service: The usage of Cloud resources is metered so that the users pay only for the help they make use of.
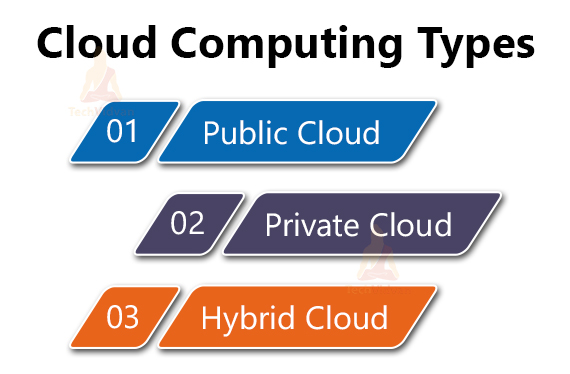
Cloud Computing Types
1. Public Cloud: The owners of Cloud resources are the third-party service provider. They have the responsibility to manage the services and are popularly known as Public Clouds. It will deliver users with resources such as servers, service, and storage over the internet.
2. Private Cloud: The organization builds its own cloud resources inside its premises/ environment in the Private Cloud. Sometimes the private Cloud can be hosted by a third service provider.
3. Hybrid Cloud: Private Cloud and Public Cloud combine together and make Hybrid Cloud. Hybrid Cloud provides flexibility and more deployment features to the business.
Cloud Services Types
1. Infrastructure-as-a-Service: In IaaS, the users can rent IT infrastructures like servers, Virtual Machines, Storage, networks, operating systems from the cloud vendor.
With IaaS, the users do not have to worry about any hardware and virtualization software. IaaS is the most flexible service, but still, it requires more effort into maintenance.
2. Platform-as-a-Service: PaaS provides a demanding environment for developing, testing, delivering, and management of applications. The PaaS vendor will take the responsibility of deploying and running.
And the developer is responsible for the application. The flexibility will get lower by using PaaS, but the management of the environment is the vendor’s responsibility.
3. Software-as-a-Service: Software-as-a-Service: SaaS will centrally host and manage the software services for end-users. They will provide the software on the internet, and it is dependent on the subscription.
The famous examples are Microsoft OneDrive, Office 365, WordPress. The main aim of SaaS is to reduce operational costs.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
1. Expense or cost: Cloud Computing will minimize the massive cost of purchasing hardware and software for an organization.
2. Speed: The user can access resources in minutes and quickly in some clicks.
3. Scalability: The user can increase and decrease the resources according to the requirements.
4. Reliability: The process of Backup and recovery is less expensive.
5. Security: Cloud vendors provide users with a range of policies, technologies, and controls. It helps to strengthen and protect data security.
6. Productivity: On Cloud, the developers can focus on productivity and do not have to worry about hardware or patching in the background environment.
Uses of Cloud Computing
1. Create Cloud-Native Application
The user can quickly add, deploy and scale the web, mobile application, and API. The user has the advantage of cloud-native technologies and approaches like containers, Kubernetes, DevOps, and many more.
2. Store, Back-up, and Retrieve Data
The user can protect their data and, in a cost, efficient manner at a vast scale. And by transferring the data on the Cloud, the user can access it from any location and from any device.
3. Stream Audio and Video
With Cloud, the users can connect with their listeners at any moment. It is possible on any device with high-definition video and audio clarity.
4. Deliver Software on Demand
It is popularly known as Software-as-a-Service. On-demand permits users to offer the latest software versions and updates to customers. It is possible at any time and anywhere.
5. Test and Build Applications
The cost and development time of applications can turn down with the help of the Cloud. It can be easily scaled up and scaled-down.
6. Analyze Data
The administrators can merge data across teams, divisions, and regions on the Cloud. They can use cloud services such as Machine Learning Tools and Artificial Intelligence Tools to understand more complex and informed decisions.
7. Embed Intelligence
Users have the facility to use intelligent models to help and engage the users with valuable insights received from data.
Risks Related to Cloud Computing
1. Security and Privacy: Security and Privacy are among the biggest worries for the users while accepting Cloud Computing. As infrastructure and management are head by a third-party provider, it is risky to store or hand over sensitive and crucial information in the Cloud.
Although Cloud vendors have high security to the data, it will be a loss for the business if a data breach occurs.
2. Lock-In: It is a challenging task for the users to switch from one cloud service provider to another.
3. Isolation Failure: There is a risk of failure in isolation mechanisms such as separation in storage, memory, and routing between various tenants.
4. Management Interface Compromise: In Public Cloud, the customer management interfaces are accessible via the internet.
5. Insecure or Incomplete Data Deletion: Sometimes, in the Cloud, there is a possibility the requested data might not get deleted. And the reasons are as follows: Extra copies of data are stored, but they are not available during the deletion time.
The disk in which data is held of various tenants might erase.
Risk, Costs, and Ethics of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is very beneficial for many users. But it has some set of risks, costs, and ethics that a user should consider. Some issues are applicable to cloud users, while some problems are applied to businesses and enterprises that use cloud services as storage.
Considerations for all Cloud Users:
1. Security: Cloud vendors provide additional security vulnerabilities compared to on-premises security. The Cloud delivers its APIs, Cloud-based credentials, and on-demand services. It authorizes hackers or unauthorized users to easily affect the services.
It will endorse that users gain information on how cloud vendors protect the client data from security threats and some additional services or practices users can implement to protect their data.
2. Data Loss: Sometimes, cloud vendors can lose stored data because of physical resources, bugs, unified synchronizing, user-generated errors, or unnoticeable errors.
While switching to cloud services, the user should look at what backup services the cloud vendor provides and be aware of whether they are provided automatically and freely. The user can wish to run backups by themselves.
3. Data Persistence: There are such times when cloud users want to forget about their personal data available in the Cloud. However, deleting data on the Cloud and ensuring its complete deletion is a time-consuming process.
It is a complicated process, and sometimes it is impossible. So, it is recommended to read the cloud policies before storing the data on the Cloud and find out their policies for deleting it.
4. Costs: While signing up for a cloud service, the users should check for billing details. And they should learn how the selected services are metered. Also, check whether the user can set notifications when the usage crosses certain limits.
It is necessary to learn and understand how billings are generated. Because the billing methods of some providers are difficult to understand.
5. Vendor Lock-in: It is challenging for the users to switch between cloud vendors after setting up. With the help of open source cloud solutions, it is somewhat more accessible for users to migrate from one cloud vendor to another.
6. Company use of Data: Cloud providers make use of customer’s data for their purposes. Such as brand marketing, data algorithms, etc. So the users must read the policies on how the data is being used and organized.
7. Company Ethics: Some giant cloud vendors have relationships worldwide, and the cloud users consider the ethics supporting the company.
Reviewing the company rules or practices like data collection, politics, environment, and other factors may help users choose the best cloud provider according to their requirements.
8. Loss of User Control and Visibility: Using third-party resources makes it difficult or nearly impossible for cloud users to keep an eye on and control environments. It can develop technical and personal conflicts.
Some technical issues can be set on with the help of monitoring, analytics tools that allow users to be updated on infrastructure performance. It will enable users to quickly respond when an issue takes place.
Trust-related matters such as personal data management can be addressed and reviewed by the company’s data policies and studying the history of the cloud provider.
Additional Business Considerations:
1. Regulation: Industries like the healthcare, finance sector have strict rules and regulations regarding the storage of client data on the Cloud. These users mostly choose hybrid Cloud and other customized IT Solutions to fulfill the rules and regulations.
Along with IT industry regulations, organizations also need to apply data protection and privacy laws of location from where the service has been accessed.
2. Complexity: Migration of data from an organization to the Cloud can be a complex task. It requires deep planning, governing structures, and continuous oversight to avoid any issues such as data loss.
And has to keep an eye on cost optimization. However, Cloud helps IT organizations reduce the cost of infrastructure, but IT experts are still required to direct and manage.
Popular Cloud Computing Vendors
In IaaS and PaaS, there are only a few popular and giant cloud providers. The list is as follows:
- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
- IBM
- Alibaba
- Digital Ocean
- VMware
- Rackspace
Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a new and emerging technology. It is at the early stage of adoption, and many companies are still planning to adopt cloud technology.
However, the organizations are comfortable with this technology as it is comfortable and reliable storing data at some location, rather than keeping the data on their campus.
Cloud vendors are pushing cloud computing as an essential aspect of digital transformation and simply focusing on the cost. Adopting to the Cloud will help organizations to leverage their business.
Summary
Cloud Computing is at the initial phases of adoption, and many companies are still considering moving their applications. Cloud Computing provides a new and broader range of opportunities to all users.