Cloud Computing- Private Clouds
The industry is leading with the help of Cloud Computing. As we know, Cloud Computing consists of three models. So, in today’s article, we will discuss the Private Cloud. It is one of the favorite cloud models in business that looks for privacy and requires a higher security layer.
What is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a set of services delivered via the internet or in a private network to only limited users instead of all users. The private Cloud is popularly known as Internal Clouds or Corporate clouds. Because it is firm to the goals of a single enterprise or organization, whereas in the public Cloud, it delivers services to many users. It provides similar advantages of public cloud-like scalability and self-service but in an exclusive architecture.
In Private Cloud, users will receive an advanced and higher level of security and privacy between both company’s firewalls and internal hosting. It helps in ensuring and securing that sensitive data are not accessible to unauthorized users. But there is one issue in the Private Cloud: the company’s IT Department is totally responsible for cost and accountability or private cloud management. Thus, in a Private Cloud, the same management staff and maintenance expenses are necessarily similar to the ownership of a traditional data center.
Private cloud planning may include hardware hosting at the organization’s facility, or the cloud service provider will take the responsibility of hosting. In industry, Virtual clouds are paid depending upon the rolling basis, but equipping hardware and storage configurations will help to maintain the benefits of a safe and absolute network.
In Private Cloud, two models carry out they are as follows:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- Platform-a-as-a-Service (PaaS)
IaaS authorizes users to utilize infrastructure resources like compute, network, and storage as a service. PaaS helps the users or organizations deliver everything from simple cloud-based applications to sophisticated applications of the company.
Private clouds offer equivalent control and security as traditional on-premises infrastructure. Here are some reasons why organizations choose personal cloud computing:
1. Security
Private cloud security is more refined since traffic to a personal cloud is usually limited to the organization’s transactions. Public cloud providers must handle traffic from many users and transactions simultaneously, thus opening a greater chance for malicious traffic. Since private clouds contain dedicated physical infrastructure, the organization has better control over the server, network, and application security.
2. Predictable performance
Because the hardware is devoted to multi-tenant, workload performance is predictable and unaffected by other organizations sharing infrastructure or bandwidth.
3. Long-term savings
Most of the time it is expensive to line up the infrastructure to support a personal cloud, it pays off within the future. Suppose a corporation already has the hardware and network required for hosting. In the following case, a private cloud is more cost-effective over time compared to paying monthly fees to use someone else’s servers on the available public cloud.
4. Predictable costs
Public cloud costs are mostly unpredictable supported usage, storage charges, and data egress charges. Private cloud costs are equivalent monthly, no matter the corporation’s workloads or what proportion of data is moved.
5. Regulatory governance
Regulations like the EU’s GDPR may dictate where data resides and where computing occurs. Additionally, organizations with sensitive data like financial or legal firms may choose private cloud storage to make sure they need complete control over personally identifiable or sensitive information.
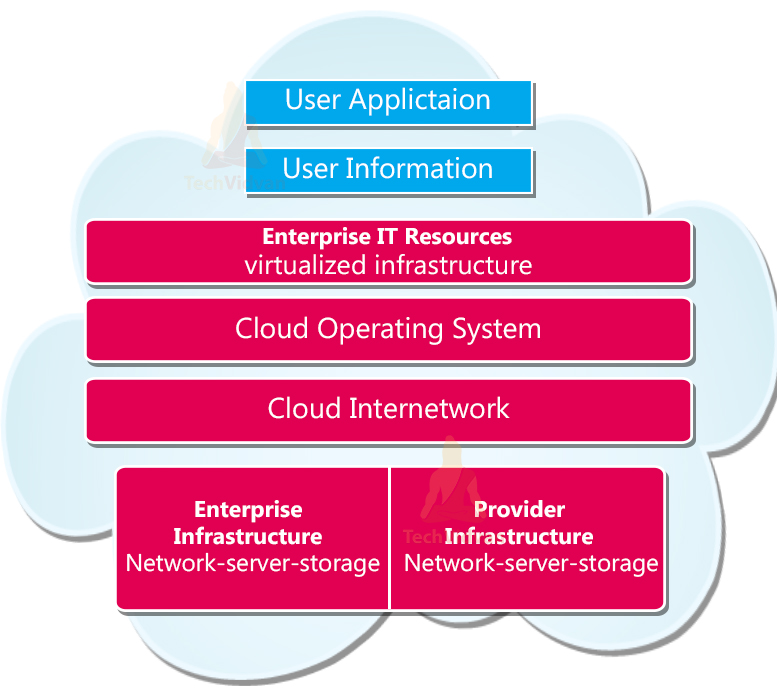
Private Cloud Model
Private Cloud authorized users to access systems and services to be within an organization. The organization takes the responsibility to operate the Private Cloud. However, the internal management is proficient by the organization itself or by a third party. The private cloud model is explained in the diagram below.
Private Cloud Architecture
Single-tenant design aside, private cloud can anticipate an equivalent technology as other cloud technologies enabling the customer to provision and configure virtual servers. Computing resources on-demand to quickly or automatically scale in response to spikes in usage and traffic, implement redundancy for top availability, and optimize resource utilization overall.
The key technologies in Private Cloud are as follows:
Virtualization played a crucial role in IT resources to be abstracted from the underlying physical hardware and pooled into unbounded resource pools of computing, storage, memory, and networking capacity. It will be portioned among multiple virtual machines (VMs) containers or other virtualized IT infrastructure elements. Virtualization enables maximum hardware utilization.
Management software provides administrators centralized control over the infrastructure and applications by running thereon. It helps to optimize security, availability, and resource utilization within the private cloud environment.
Automation helps speed the tasks such as server provisioning and integrations done manually and repeatedly. Automation also reduces the role of human intervention and thus makes a self-service resource delivery possible.
How Private Cloud Works?
A Private Cloud is a single-tenant environment which means the organizations do not share their resources with other clients or users. These resources can be hosted and managed in multiple methods. The Private Cloud can sometimes be built on resources and infrastructure already present in the organization’s on-premises data center. Otherwise, new and separate infrastructure can be developed with the help of a third-party provider.
But there are some cases in which the single-tenant environment is being validated individually by using virtualization software. But in any case, the private Cloud and its resources are loyal towards a single user or tenant. The Private Cloud is one of the cloud deployments models. Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud share essential components of cloud infrastructure.
Who Uses Private Cloud Infrastructure?
Private cloud is very successful and famous for highly regulated industries and government agencies. Because they want their sensitive and crucial records protected, like those within the medical field. Similarly, technology companies that need robust control and security over their IT workloads and, therefore, the underlying infrastructure can enjoy having a personal cloud. Some serious industries like medical organizations require a private cloud instead of a public cloud.
Organizations have multiple reasons beyond privacy that specify why a growing number of companies have adopted the private cloud model.
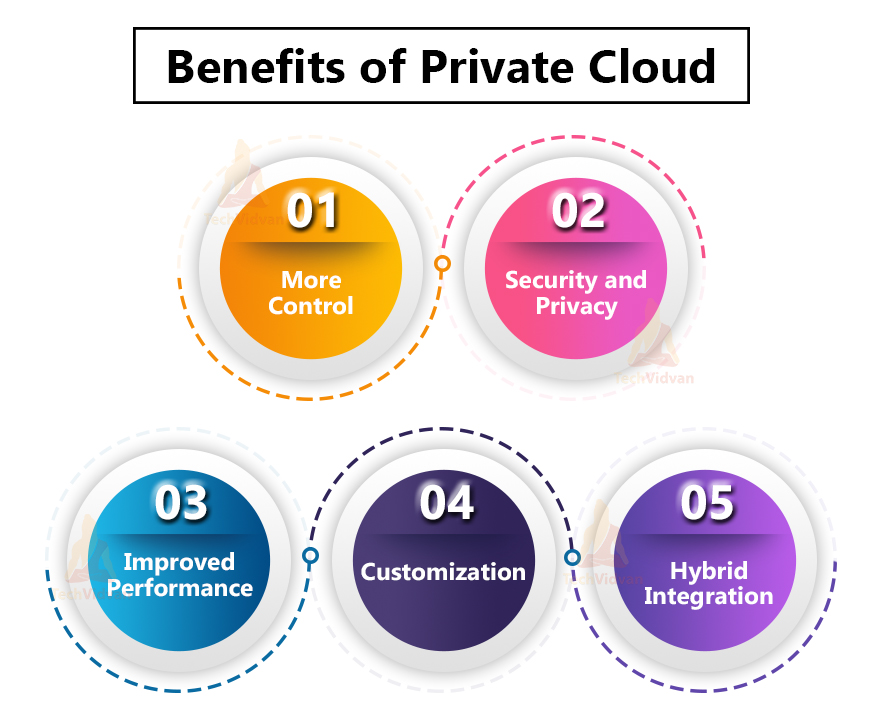
Benefits of Private Cloud
1. More Control
The private Cloud offers more control over the resources and hardware than the public Cloud. This is because only authorized users have access.
2. Security and Privacy
The main advantage of the Private Cloud is its security and privacy. It consists of improved and additional security levels compared to Public Cloud.
3. Improved Performance
Users adopting Private Cloud experience better performance with improved speed and space.
4. Customization
Private Cloud offers a complete configuration to the organization. A private cloud is built under the guidance of an experienced on-site cloud architect, which means organizations can specify the exact required environment to run applications. Hosted Private cloud is beneficial, and there is no requirement for on-premises setup. In this scenario, the business and vendor will work together to design and manage the Cloud.
5. Hybrid Integration
Sometimes an application requires additional computing resources. In this case, hybridization helps extend the private Cloud resources into a public cloud to maintain uptime without installing additional servers. It can be a cost-effective solution for businesses who require a private Cloud security level and want to function as a public cloud.
Challenges in Private Cloud
1. High Cost
Private Cloud is costlier than Public Cloud as the setup cost, and maintenance cost are expensive.
2. The restricted area of Operations
In a Private Cloud, the operations are finite within an organization, so the functions are finite.
3. Limited Scalability
Scaling in Private Cloud can be hosted within the internal resources capacity of an organization.
4. Skilled People
Skilled People are significant for an organization to manage and operate cloud services.
5. Up-Front Cost
Fully Private Clouds are hosted on-site and require heavy capital. In a Private Cloud, the hardware requirements can be costly, and an expert cloud architect is necessary for setting up, maintaining, and managing the environment.
6. Capacity Utilization
Organization is responsible for maximizing the utilization capacity in Private Cloud.
Is a private cloud more secure than a Public Cloud?
Private clouds are usually safer than public clouds, with one crucial caveat: Organizations must proactively make sure that security is robust and up so far to reap the advantages of personal cloud. As long as a corporation isn’t complacent about safety, the private cloud offers many benefits for security. Since private clouds are finite to specific physical machines, they are often easier to make certain physical security.
Most private clouds sit behind a fringe firewall and are accessed through personal, secure network links instead of the general public internet. Additionally, the degree of control a business has over its private cloud can make it easier to realize regulatory compliance and governance mandates.
Top Private Cloud Providers
Below is the list of top and leading Private Cloud Providers, and they are as follows:
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- Cisco
- Microsoft
- VMware
- Dell EMC
- Oracle
- IBM
- Red Hat
Conclusion
Thus, in today’s article, we have learned about the Private Cloud along with its work. Private Cloud is beneficial for Organizations for security concerns. Simultaneously, there are some disadvantages such as costing and more. So we have tried to provide all the essential information on the Private Cloud.